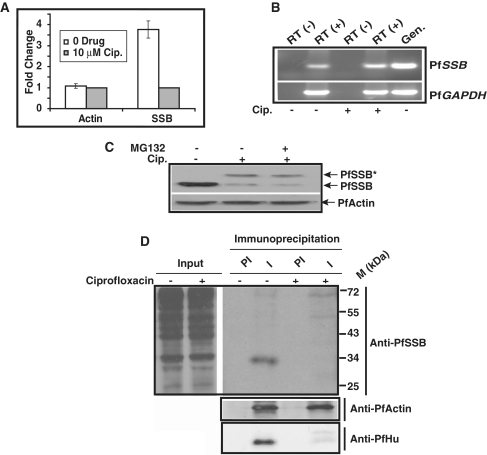
Figure 6.
(A) Comparison of expression level of PfSSB and PfActin in the absence and presence of ciprofloxacin for three different set of experiments. Western blot experiments were performed using parasite lysate obtained from ciprofloxacin (10 μM) treated or untreated parasites in the presence of antibodies against PfSSB and PfActin. The relative intensity of the bands was measured using densitometry scanning followed by graphical representation of them to show the fold change in the expression level. (B) RT-PCR analysis of PfSSB and PfGAPDH transcript level from the parasites treated with cip. or untreated parasites. RT (−) indicates the cDNA prepared from total RNA samples treated without reverse transcriptase. (C) Western blot analysis to evaluate the effect of proteosome inhibitor MG132 on PfSSB expression. Parasites treated with ciprofloxacin were further treated with MG132 during second life cycle before harvesting for western blot analysis. The results indicate that treatment with MG132 does not change the PfSSB protein level. The same blot was reprobed with anti-PfActin antibodies as control. (D) Status of newly synthesized PfSSB during second life cycle following ciprofloxacin treatment. Ciprofloxacin treated or control parasites were incubated in the presence of 35S-methionine for 3 h during the trophozoite stage of the second life cycle (∼68 h post-drug treatment) followed by immunoprecipitation analysis of PfSSB or PfActin or PfHU proteins using respective pre-immune (PI) or immune (I) sera from control or drug treated parasite lysate. The total parasite lysate obtained from untreated and drug treated 35S-methionine labelled parasites were loaded as input (inp.). The results indicate that the expression of newly synthesized PfSSB and PfHU is affected significantly without affecting the expression of PfActin under the same experimental conditions.