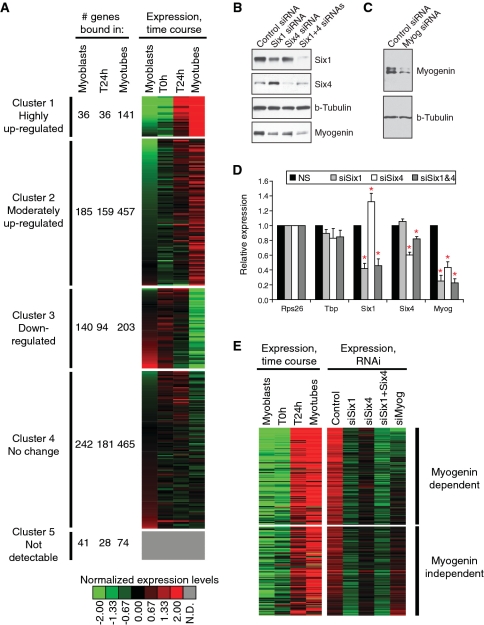
Figure 3.
SIX1 binding is associated to gene activation during myoblast differentiation. (A) Heat-map representing the expression profiles of SIX1 target genes identified in our ChIP-on-chip, grouped in clusters formed using all genes represented on the expression profiling microarrays. A legend giving the color code for normalized gene expression values is given at the bottom. The color grey is assigned to genes with undetectable (N.D.) expression in C2C12 cells. For each of five clusters, the number of targets bound in each condition (myoblasts, T24 h or MT) is given. SIX1 target genes not represented on expression arrays were omitted from this analysis. (B) Protein expression levels of SIX1 and SIX4 after their knock-down using siRNA duplexes. Myogenin levels are shown as well. Beta-tubulin levels are shown as a loading control. (C) Expression levels of myogenin after its knock-down by siRNA. Beta-tubulin levels are shown as a loading control. (D) mRNA expression levels of Six1 or Six4 after their knock-down, as measured by qRT-PCR. Data were normalized relative to the Rps26 gene. The levels of Tbp (TATA-binding protein) mRNA serve as an additional invariant control. The data represent the average of at least three biological replicates. Error bars: SEM. Asterisks indicate a Student’s paired t-test P-value lower than 0.05, when compared with the control siRNA duplex. (E) Heat-map representing the expression levels of SIX1 target genes affected by knock-down of SIX1 (2-fold change or more) during normal differentiation (left-hand side) or after the knock-down of SIX1, SIX4, SIX1 and SIX4 or MYOG (right-hand side). The color code is the same used in panel A. Genes are ranked from top to bottom in decreasing order of down-regulation after myogenin knock-down. Those for which the knock-down of MYOG gave a 50% or more reduction in expression are represented in the top portion (MYOG-dependent), otherwise they lie in the bottom portion (MYOG-independent).