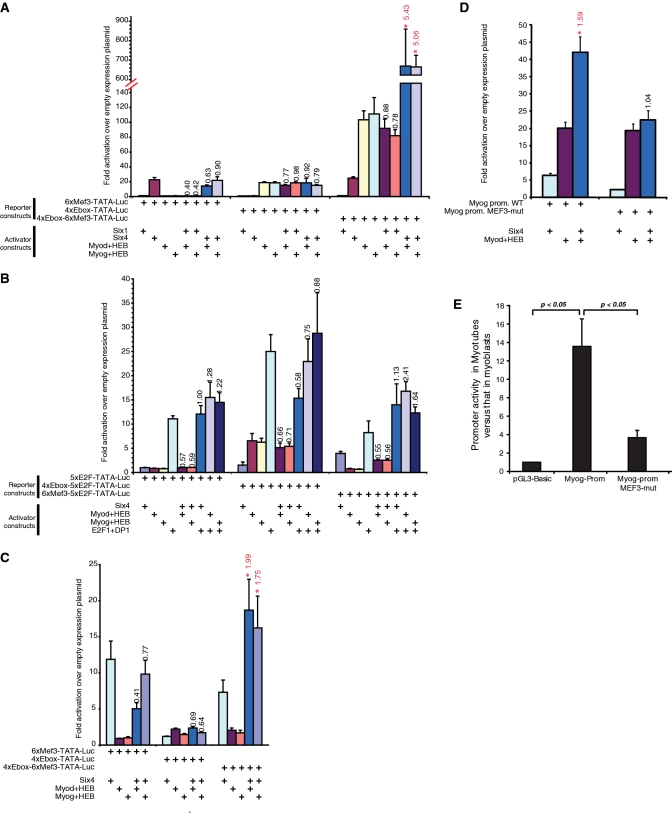
Figure 4.
Transcriptional synergism between SIX and MRF transcription factors. (A) 293T cells were transfected with the indicated firefly luciferase reporter constructs and various combinations of expression plasmids for transcription factors, as indicated. A plasmid driving the expression of renilla luciferase was used as internal control, for normalization purposes. Normalized firefly luciferase activities were divided by those obtained in cells transfected with the empty expression plasmid, giving values of fold activation over empty plasmid. Each experiment was performed a minimum of three times. Histogram values represent the average ± SEM of all replicates. Note the axis break and change of scale. For conditions with a combination of transcriptional activators, the synergy value is indicated above the histogram bar. Synergy values that are statistically significant (P < 0.05 by one-tailed paired t-test) are marked in red with an asterisk. (B) The experiment was performed as in panel A, but using different combinations of reporter constructs and transcriptional activators. Synergy is indicated as in panel A. (C) Transcriptional activity of SIX factors and the MRFs in C2C12 myoblasts. Cells were transfected with the indicated firefly luciferase reporter constructs and various combinations of expression plasmids for transcription factors, as indicated. Samples and data were processed as in panel A. (D) Transcriptional activity of SIX4 and MYOD in 293T cells transfected with a reporter construct consisting of the myogenin proximal promoter fused to the luciferase gene, or with a similar construct where the MEF3 site has been mutated. Samples and data were processed as in panel A. (E) Luciferase activity in cells transfected with the wild-type myogenin promoter reporter construct or a version with its MEF3 site mutated, or the empty luciferase plasmid (pGL3-basic). The results show the ratio of luciferase activity in MT divided by that in myoblasts.