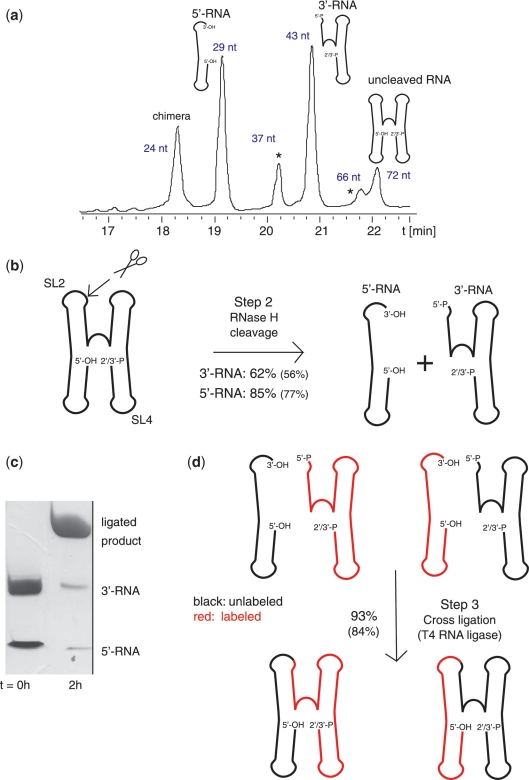
Figure 3.
RNase H cleavage (Step 2) and direct non-splinted cross-religation using T4 RNA ligase (Step 3). (a) Denaturing anion-exchange HPLC profile of fragments obtained by site-specific RNase H cleavage in SL2 between A29 and C30 of the RsmZ RNA (60 nmol reaction). The RNase H cleavage was performed with a chimera/RNA ratio of 0.75:1. The different fragments obtained by RNase H cleavage are shown on the top of their corresponding peak. Side-products occurring because of ‘unspecific’ cleavage in SL4 are marked by asterisks (see Supplementary Figure S3). The retention time of the HPLC profile is indicated on the y-axis. The purification conditions used are presented in the methods section. (b) Scheme of RNase H cleavage reaction and corresponding reaction yields. The yield of the cleavage reaction before HPLC purification is indicated, the values in brackets are expressing the yield after purification. The site of cleavage is shown by scissors. (c) Analytical 16% denaturing PAGE gel of the ligation reaction. Left lane: 400 pmol of each 5′-RNA (29 nt) and 3′-RNA (43 nt) before ligation, right lane: after ligation. (d) Reaction scheme and corresponding reaction yields for T4 RNA ligase mediated non-splinted cross-ligation of both a labeled (in red) and an unlabeled (in black) fragment, respectively. The ligation yield determined with a reaction using only unlabeled fragments is indicated.