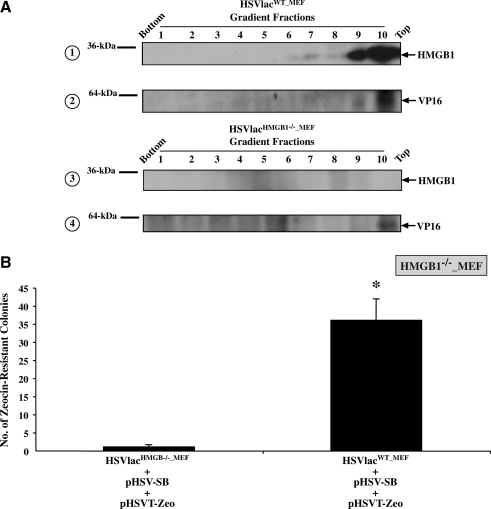
FIG. 4.
HMGB1 protein is incorporated into the viral tegument during helper virus-free amplicon packaging and facilitates SB-mediated transposition. (A) HSVlac amplicon vector stocks separately packaged in MEF-derived HMGB1 wild-type and HMGB1-deficient cell lines (designated HSVlacWT_MEF and HSVlacHMGB1–/–_MEF, respectively) were treated with 1% NP-40 and subjected to rate zonal centrifugation in a linear sucrose gradient. Gradient fractions were analyzed by Western blotting to determine the fractions containing HMGB1 (panels 1 and 3). Subsequently, the samples were analyzed for the presence of the HSV tegument protein VP16 (panels 2 and 4). (B) HMGB1-deficient MEF cells were separately transduced with HSVlacWT_MEF and HSVlacHMGB1–/–_MEF at an MOI of 1. Four hours posttransduction, the cells were cotransfected with pHSVT-Zeo and pHSV-SB amplicon plasmids at a 1:1 mass ratio. On incubation for 48 hr, the cells were trypsinized and seeded at a 1:13 dilution on 100-mm dishes containing medium supplemented with Zeocin (100 μg/ml) (n = 3 per condition) and incubated for 14 days. Zeocin-resistant colonies were enumerated via methylene blue staining. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean and statistical analysis was conducted by Student t test. *denotes p < 0.05.