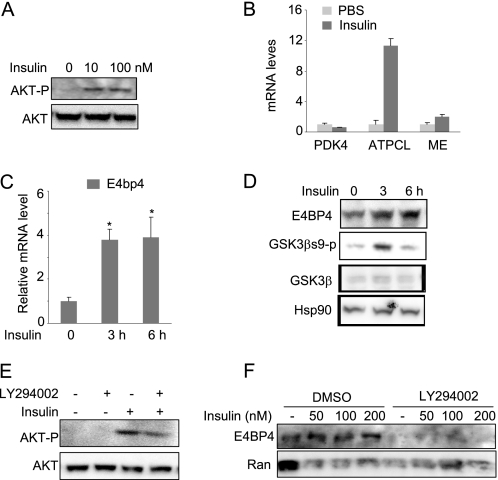
FIGURE 5.
Insulin up-regulates the expression of E4BP4 through AKT activation in liver cells. A, insulin-induced AKT phosphorylation in Hepa1c1c-7 cells. Both total and phosphorylated AKT proteins were detected by immunoblotting. B, Q-PCR analysis of the mRNA levels of Pdk4, ATP citrate lyase, and malic enzyme (ME) in the insulin-treated Hepa1C1C-7 cells. C, insulin up-regulates the gene expression of E4bp4 in a time-dependent manner in Hepa1c1c-7 cells. Confluent Hepa1c1c-7 cells were treated with insulin at 200 nm for 0, 3, and 6 h before harvest. The mRNA level of E4bp4 was determined by Q-PCR. Results are expressed as mean ± S.D. (error bars) (n = 3). *, p < 0.05. D, insulin up-regulates the E4BP4 protein levels in freshly isolated primary mouse hepatocytes. Cells were treated with insulin at 200 nm for 0, 3, and 6 h. The protein levels of E4BP4, GSK3β, GSK3βs9p, and loading control Ran were detected by specific antibodies. E, pretreatment with PI3K inhibitor LY294002 (50 μm) blocks AKT phosphorylation by insulin in Hepa1c1c-7 cells. The control was treated with DMSO. F, AKT inhibition blocks the insulin-induced E4BP4 protein expression in Hepa1C1C-7 cells. Cells were treated with either DMSO or LY294002 for 2 h before insulin treatment at various concentrations for 12 h. An immunoblot was used for detecting E4BP4 protein levels.