FIGURE 6.
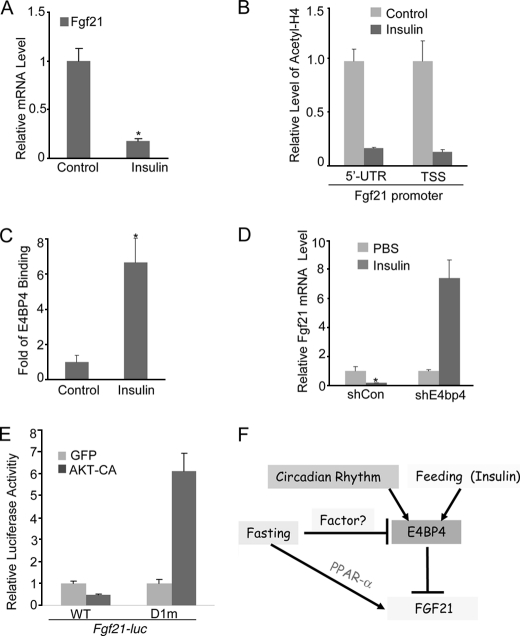
Insulin suppresses Fgf21 via the induction of E4BP4 in liver cells. A, insulin suppresses the Fgf21 expression in Hepa1c1c-7 cells. Confluent Hepa1c1c-7 cells were first synchronized by 50% horse serum for 2 h and incubated at serum-free medium for another 6 h. Cells were then treated with 200 nm insulin for 12 h before Fgf21 Q-PCR. Results are expressed as mean ± S.D. (error bars) (n = 3). *, p < 0.05. B, insulin treatment increases the levels of acetylated H4 around the Fgf21 promoter regions. Confluent Hepa1c1c-7 cells were treated as in A before ChIP analysis with specific antibodies. Results are expressed as mean ± S.D. (n = 3). C, insulin treatment stimulates the recruitment of E4BP4 onto the Fgf21 promoter. Confluent Hepa1c1c-7 cells were treated as in A before a ChIP assay with anti-E4BP4 antibody. D, E4BP4 is required for the insulin-induced suppression of Fgf21 in liver cells. After synchronization by 50% horse serum for 2 h and incubation in serum-free medium for another 6 h, Hepa1c1c-7 cells stably expressing either shRNA or E4bp4 shRNA were then treated with insulin at 200 nm for 12 h before Fgf21 mRNA analysis. Results are expressed at mean ± S.D. (n = 3). *, p < 0.05. E, AKT activation represses the luciferase activity driven by the wild type Fgf21 promoter but not by the E4BP4 binding site-deleted mutant. A constitutively active AKT was co-transfected into Hepa1c1c-7 cells along with either WT Fgf21-luc or D1m Fgf21-luc. The relative luciferase activities 48 h post-transfection are presented as mean ± S.D. (n = 3). F, model for the regulation of hepatic FGF21 expression by E4BP4. Both insulin and feeding induce E4bp4 to regulate the Fgf21 circadian oscillation upon food intake. E4BP4 directly binds to a distal D-box element of the Fgf21 promoter to suppress its expression. As a first order circadian output gene, E4BP4 links the circadian rhythm to liver metabolism.