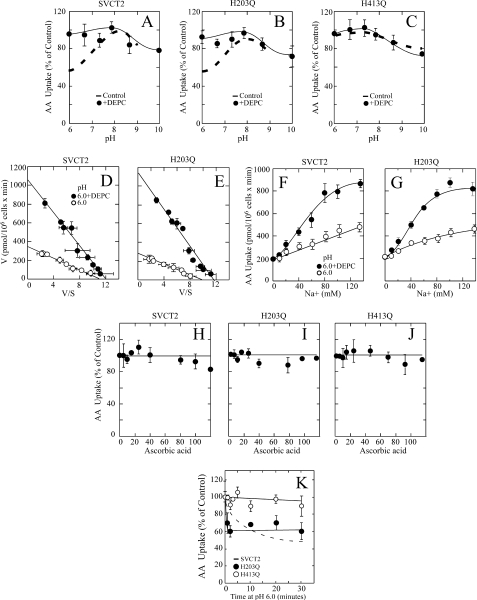
FIGURE 10.
SVCT2 and mutants H203Q and H413Q; pH sensitivity and DEPC and ascorbic acid effect. Forty-eight hours after transfection, the cells were assayed for ascorbic acid transport. A–C, effect of pH on ascorbic acid transport in HEK-293 cells expressing SVCT2 (A), mutant H203Q (B), or mutant H413Q (C) and treated with (●) or without (dashed line) 30 μm DEPC. D–E, ascorbic acid transport kinetics at pH 6.0 in HEK-293 cells expressing SVCT2 (D) or mutant H203Q (E) and treated with (●) or without (○) 30 μm DEPC. F and G, Na+ cooperativity of ascorbic acid transport at pH 6.0 in cells expressing SVCT2 (F) or mutant H203Q (G) and treated with (●) or without (○) 30 μm DEPC. H–J, effect of ascorbic acid on the effect of DEPC on the transporter pH sensitivity. Transfected HEK-293 cells expressing SVCT2 (H), mutant H203Q (I), or mutant H413Q (J) were incubated for 30 min with 30 μm DEPC in the presence of increasing ascorbic acid concentrations, washed, and assayed for ascorbic acid transport at pH 6.0. K, time course of the effect of acid pH. SVCT2 (dashed line), mutant H203Q (●), and mutant H413Q (○) were incubated at pH 6.0 for the indicated times and assayed for ascorbic acid transport at pH 6.0. Transport data correspond to the means ± S.D. (error bars) of one experiment of two performed in triplicate.