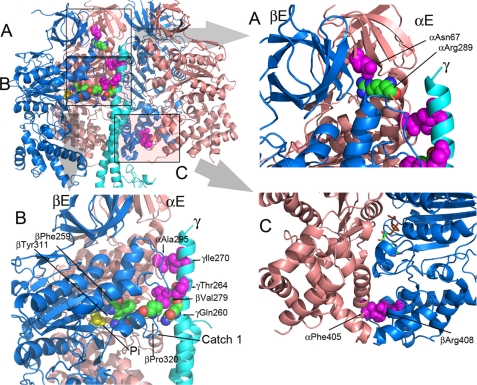
FIGURE 1.
Positions of the mgi residues in the structure of the yeast F1 ATPase. The mgi residues are colored magenta, and the atoms are shown as spheres. The atoms of interacting residue are shown as spheres but colored as defined by the atom type. The panel in the upper left shows a cartoon representation of the α- (salmon) and β- (blue) subunits forming the E and DP sites along part of the γ-subunit (light blue). In the upper left panel, the areas shaded and labeled as A, B, and C represent the regions shown in A, B, and C. A, the region illustrates the mgi residue, αAsn67 and its interaction with αArg289. B, mgi residues, αAla295 and γIle270 form interacting pairs, along with βVal279 and γThr264. Phosphate (Pi) is shown in yellow. αAla295 is located in the collar region of the α-subunit, and βVal279 is in the collar region of the β-subunit. βPhe259 and βTyr311 are critical interacting pairs that aid in forming the active site. C, mgi residues αPhe405 and βArg408 make critical contacts in TP and DP pairs of yF1II, but not yF1I. The nucleotide is shown as a stick model in atom-defined colors.