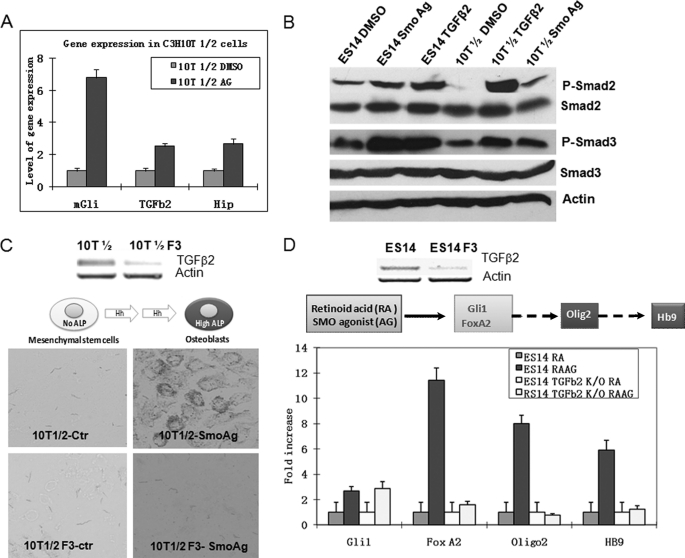
FIGURE 2.
Functional requirement of TGFβ2 for Hh signaling-mediated biological processes. A, real-time PCR analyses of gene expression of Gli1, Hip, and TGFβ2 in C3H10T1/2 cells following treatment with SMO agonist purmorphamine (indicated as Ag in the figure) for 24 h. Cells treated with purmorphamine were compared with those treated with DMSO for gene expression of mGli1, Hip, and TGFβ2 by real-time PCR. Error bars indicate S.D. B, detection of SMAD2 and SMAD3 phosphorylation in cells treated with purmorphamine. Mouse ES cells or C3H10T1/2 cells were incubated with purmorphamine or DMSO for 24 h, and levels of SMAD2/3 phosphorylation (P-Smad2/P-Smad3) were analyzed by Western blotting. The level of β-actin and the total proteins of SMAD2/3 were used as the controls. C, the requirement of TGFβ2 for Hh signaling-mediated osteoblast cell differentiation. Expression of TGFβ2 was down-regulated by shRNA-mediated gene silencing. Of the five shRNA clones, we found that three (F3, F5, and F7) were effective in silencing TGFβ2 expression, whereas two were not. We compared cells with down-regulation of TGFβ2 with either parental cells or cells with ineffective shRNAs for their abilities to express ALP. This figure shows TGFβ2 expression after F3 shRNA knockdown in C3H10T1/2 cells as compared with an ineffective clone (top) and their levels of alkaline phosphatase (bottom). F3 shRNA-derived cells were unable to express ALP, whereas the control (Ctr) cells had a high level. F5- and F7-derived cells were similar to F3-derived cells (data not shown). The level of ALP was also measured by optical density following incubation with the substrates for different time points (supplemental Fig. S4). D, the effect of TGFβ2 in Hh signaling-mediated motor neuron differentiation. Mouse ES cells were induced to differentiate into motor neurons after incubation with retinoic acid and purmorphamine. We examined TGFβ2 down-regulated cells with either parental cells or the control shRNA-derived cells for expression of motor neuron differentiation markers (Hb9, Olig2, and FoxA2) after induction. Cells with low expression of TGFβ2 (top) continued to express Gli1 in response to purmorphamine but failed to express Hb9, Olig2, and FoxA2 (bottom). All three shRNA-derived ES14 cells had similar results (not shown).