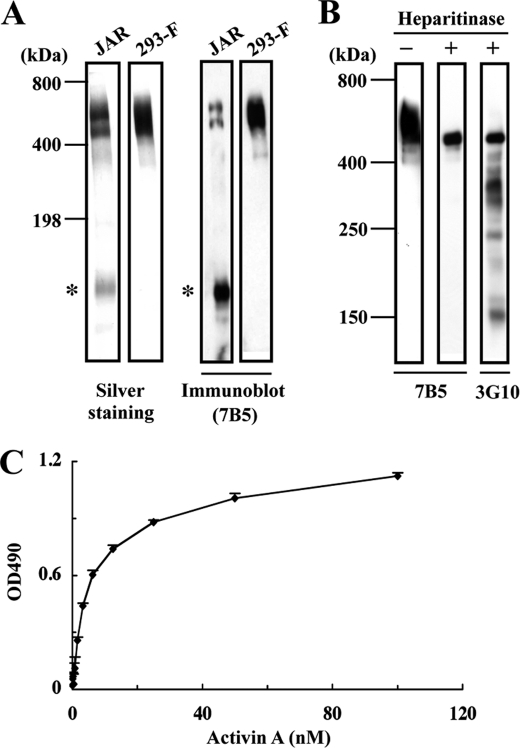
FIGURE 2.
Binding of activin A to recombinant perlecan. A, SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analyses of human perlecan purified from the culture supernatants of JAR human choriocarcinoma cells and 293-F cells transfected with a full-length human perlecan cDNA. Both recombinant and JAR-derived perlecans produce bands migrating in the 500–600 kDa region that are recognized by an anti-perlecan mAb (7B5). A proteolytically degraded fragment (asterisks) is detected in JAR-derived perlecan but not recombinant perlecan. B, heparitinase treatment of recombinant perlecan. Recombinant perlecan was treated with heparitinase, followed by immunoblotting with anti-perlecan mAb 7B5 or with mAb 3G10, which recognizes a neo-epitope derived from heparan sulfate chains after heparitinase digestion. C, binding of activin A to recombinant perlecan. Recombinant perlecan was coated at 5 nm and incubated with increasing concentrations of recombinant activin A. Activin A bound to perlecan was quantified as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Each column and bar represent the mean and S.D. of triplicate assays, respectively.