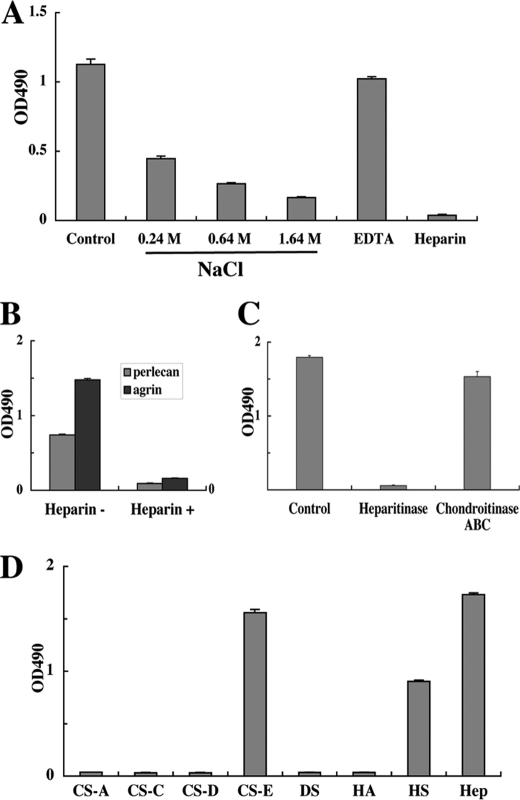
FIGURE 3.
Involvement of heparan sulfate chains in activin A binding to perlecan. A, inhibitory effects of high salt concentrations, the chelating agent EDTA and heparin on the perlecan-binding activity of activin A. Recombinant activin A (50 nm) was incubated in 96-well microtiter plates coated with JAR-derived perlecan (10 nm) in the presence of increasing concentrations of NaCl (0.24–1.64 m), EDTA (5 mm), or heparin (10 μg/ml) for 1 h, followed by quantification of bound activin A as described under “Experimental Procedures.” B, heparin (10 μg/ml) inhibits the binding of activin A to recombinant perlecan and agrin, both of which were expressed in 293-F cells. C, abrogation of the perlecan binding activity of activin A after heparitinase treatment of perlecan. JAR-derived perlecan coated on 96-well microtiter plates at 10 nm was treated with heparitinase or chondroitinase ABC at 37 °C for 3 h, followed by incubation with recombinant activin A (50 nm) for 1 h. D, solid-phase binding assays of activin A with a panel of GAGs derivatized with phosphatidylethanolamine (PE-GAGs). PE-GAGs were coated at 20 μg/ml overnight and incubated with recombinant activin A (50 nm) for 1 h. Recombinant activin A bound to perlecan was quantified as described under “Experimental Procedures.” CS-A, chondroitin sulfate-A; CS-C, chondroitin sulfate-C; CS-D, chondroitin sulfate-D; CS-E, chondroitin sulfate-E; DS, dermatan sulfate; HA, hyaluronic acid; HS, heparan sulfate; Hep, heparin. Each column and bar represent the mean and S.D. of triplicate assays, respectively.