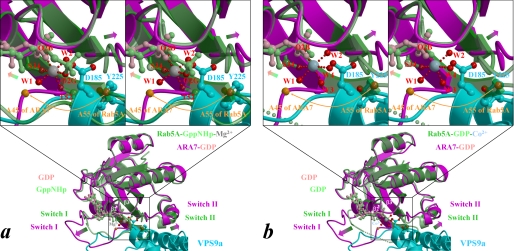
FIGURE 4.
Expected structural changes of ARA7 upon binding to VPS9a. a and b, the form B of Rab5A·GppNHp·Mg2+ (Protein Data Bank entry 1R2Q; green) and Rab5A·GDP·Co2+ (chain B of Protein Data Bank entry 1TU4; green), respectively, are superimposed on the structure of ARA7·GDP (magenta) bound to VPS9a (cyan). A subset of the VPS9a structure, including Asp185 and Tyr225, whose side chains are drawn as ball-and-stick models, is displayed for clarity. Nucleotides in Rab5A and ARA7 are drawn as ball-and-stick models and colored in light green and pink, respectively. Structural differences between the switches and the phosphate-binding cassette are indicated by green-to-magenta arrows. The interswitch region of ARA7 is unzipped by hydrophobic contacts with VPS9a (Fig. 3), and the unzipping is represented by the Cα positions of the ARA7 Ala45 and Rab5A Ala55, indicated by orange spheres and an arrow. The side-chain oxygens of VPS9a and the oxygens coordinated to Co2+ (blue-gray sphere), or Mg2+ (gray sphere), of Rab5A are drawn as red spheres with red dots indicating coordination to the metal.