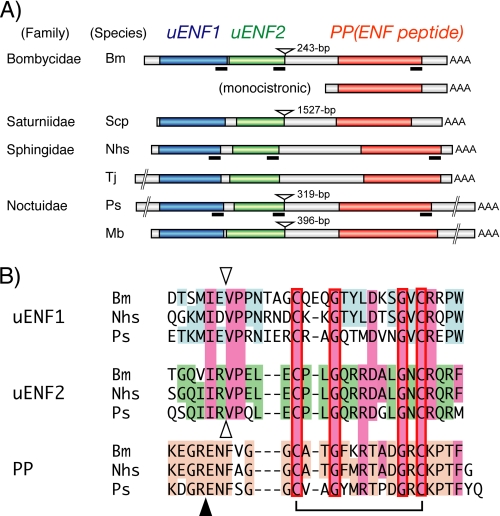
FIGURE 2.
The uENF1-uENF2-PP tricistronic mRNA is expressed in a variety of moths. A, structural organization of the tricistronic mRNA identified from six moths is shown. The uENF1, uENF2, and PP (ENF peptide) ORFs are indicated using blue, green, and orange boxes, respectively. The structure of the B. mori PP monocistronic mRNA is also shown. Deduced amino acid sequences corresponding to the underlined portions of the mRNA are compared in panel B. The inverted triangles show the positions where the introns were found in the respective genes. The length of each intron is indicated on the right side of each inverted triangle. Bm, B. mori; Scp, S. cynthia pryeri; Nhs, N. himachala sangaica; Tj, T. japonica; Ps, P. separata; Mb, M. brassicae. B, alignment of the C termini of uENF1, uENF2, and PP (ENF peptide) precursor of three moths is shown. Conserved amino acid sequences are colored. The closed triangle represents the site where the PP precursor is cleaved to form the mature PP, and the inverted open triangles indicate the corresponding putative cleavage sites for uENF1 and uENF2. A disulfide bond formed between the conserved cysteine residues of PP (ENF peptide) is also indicated. The mature PP and putative mature peptides of uENF1 and uENF2 were synthesized and used in the bioassay shown in Fig. 9.