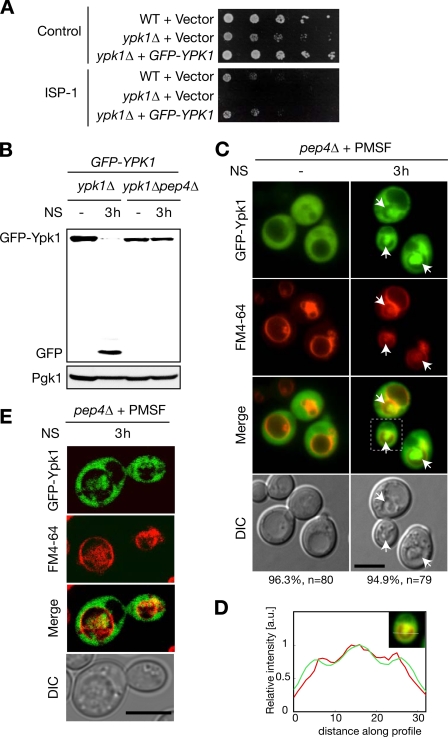
FIGURE 2.
GFP-Ypk1 is sorted into vacuoles upon nitrogen starvation. A, complementation assays on GFP-YPK1 in ypk1Δ background. WT or ypk1Δ cells transformed with vector (pRS415) control or pRS415-GFP-YPK1-harboring ypk1Δ cells were plated on leucine-deficient SD plates containing methanol or 250 ng/ml ISP-1 to examine complementation of the proliferative defect or ISP-1 resistance, respectively. The plates were incubated at 30 °C for 2 days. B, effect of N-terminal GFP fusion on nitrogen starvation-mediated vacuolar proteolysis of Ypk1. Expression of GFP-Ypk1 and cleaved GFP were analyzed by Western blotting with an antibody against GFP in ypk1Δ or ypk1Δpep4Δ cells transformed with pRS415-GFP-YPK1 upon nitrogen starvation (NS). C and D, fluorescence microscopic analyses of GFP-Ypk1 in nitrogen-starved pep4Δ cells. Logarithmically growing pep4Δ cells harboring pRS415-GFP-YPK1 were pulsed with FM4-64 lipophilic dye for 1 h and chased for 1 h. The FM4-64-labeled cells were starved of nitrogen in the presence of PMSF. Localization of GFP-Ypk1 fluorescence was examined 3 h after nitrogen starvation. Differential interference contrast (DIC) images were utilized to locate exaggerated structures inside vacuoles (arrows). Percentages noted below the images represent frequencies of the indicated phenotypes. Fluorescence intensity collected along a line was normalized with the maximum intensity in each channel. Relative fluorescence intensities of GFP-Ypk1 (green) and FM4-64 (red) were plotted (D). E, confocal microscopic analyses of GFP-Ypk1 in nitrogen-starved pep4Δ cells. Logarithmically growing pep4Δ cells harboring pRS415-GFP-YPK1 were pulse-chased with FM4-64 and starved of nitrogen as described in C. Cell culture was terminated by NaF and NaN3 treatment on ice as described under “Experimental Procedures,” and the fluorescence was immediately imaged by confocal microscope after this treatment. See also supplemental Movie 1. Bars, 5 μm. a.u., arbitrary units.