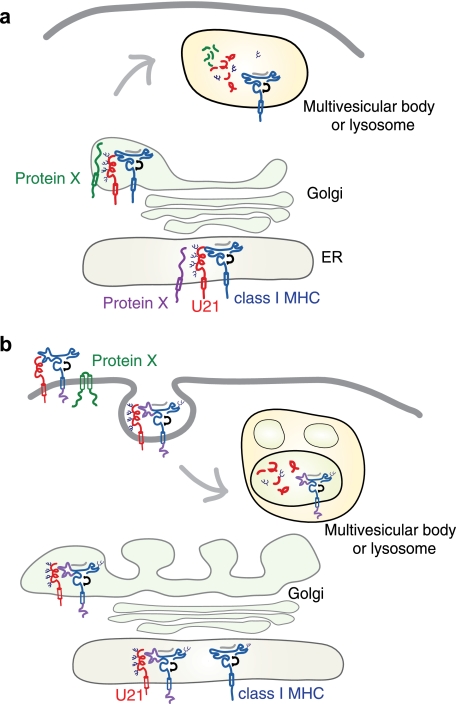
FIGURE 14.
Models depicting U21-mediated diversion of class I MHC molecules to the lysosomal compartment. U21 (red) associates with and diverts class I MHC molecules (blue) to a lamp1- and lamp2-positive lysosomal compartment. In a, U21-class I MHC complex associates with a cellular protein, Protein X (green or purple), which contains lysosomal targeting information. The association with Protein X could occur in the ER (purple) or later on in the biosynthetic pathway (green), accounting for a short-lived association with U21, and the lack of apparent coimmunoprecipitation of U21 with Protein X. Trafficking to lysosomes may involve a direct route from the Golgi to the lysosomal compartment or may involve arrival at the plasma membrane and subsequent routing through endosomes (depicted in b). In b, U21 (red) associates with class I MHC molecules and causes a conformational change in the class I molecule that is transduced through the membrane to the cytoplasmic tail. Through its lumenal association with U21, the cytoplasmic tail of the class I MHC molecule is somehow rendered competent to be modified by a Protein X (green), which then targets the complex of U21 and class I to an endolysosomal compartment.