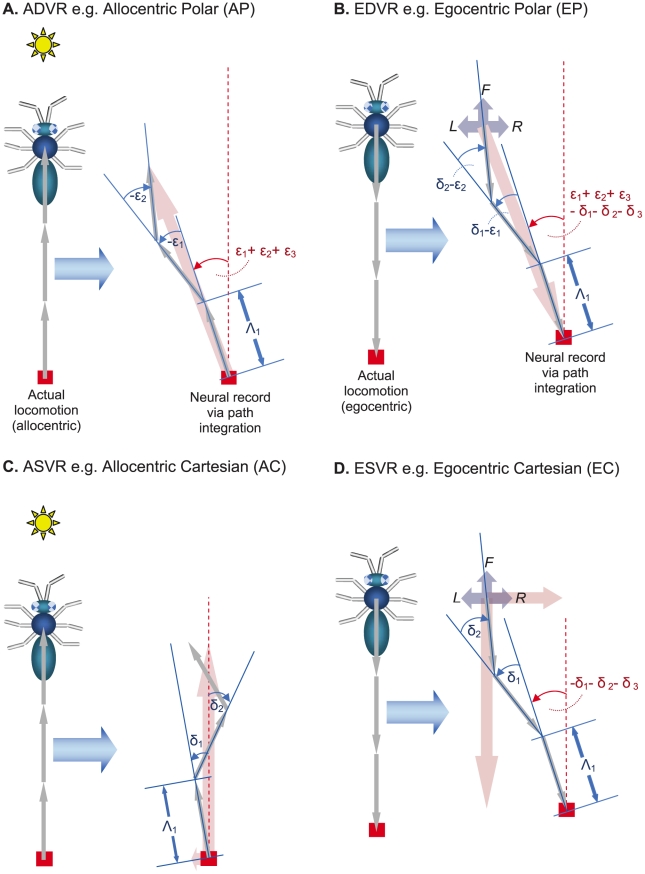
Figure 3. The effect of noise in different neural representations of space during PI.
Note that each complete path is shown in representational space for clarity, but the process of PI only requires the maintenance of the current net position, ignoring previous steps. The examples shown are (A) allocentric dynamic vectorial representation (ADVR) e.g. allocentric polar (AP), (B) egocentric dynamic vectorial representation (EDVR) e.g. egocentric polar (EP), (C) allocentric static vectorial representation (ASVR) e.g. allocentric Cartesian (AC) and (D) egocentric static vectorial representation (ESVR) e.g. egocentric Cartesian (EC). Input rotational errors are denoted δ, update errors are denoted ε, and representational step lengths are denoted Λ. Actual locomotion is represented by three gray arrows in an allocentric (A and C) or egocentric (B and D) reference frame. The thick pink arrows represent distances, and egocentric forward (F), left (L) and right (R) are labelled for clarity. Other conventions are as in previous figures. See text for details.