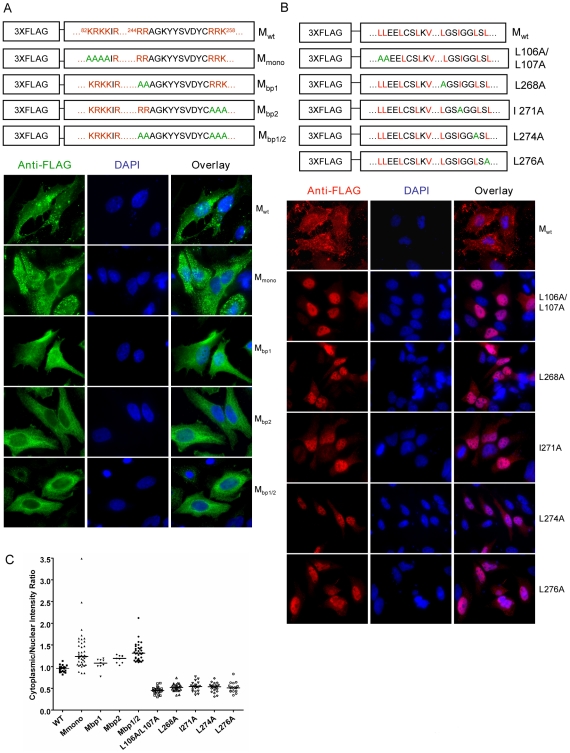
Figure 2. Mutagenesis studies of potential nuclear localization signals (NLSs) and nuclear export signals (NESs) in NiV-M.
Positively charged amino acid residues in the predicted monopartite and bipartite NLSs (A) or key leucine/isoleucine residues in the potential NESs (B) were mutated to alanines using site-directed mutagenesis. HeLa cells expressing the indicated proteins were stained with an anti-FLAG monoclonal antibody as well as DAPI. Representative fields are shown in (A) and (B), and (C) shows the quantification of cytoplasmic/nuclear fluorescence intensity (C:N) ratios for ∼10–50 individual cells analyzed for each mutant as described in Materials and Methods . Compared to Mwt, statistically significant increases in C:N ratios were observed for Mbp1 (p<0.01), Mbp2 (p<0.0001) and Mbp1/2 (p<0.0001) (unpaired t-test).