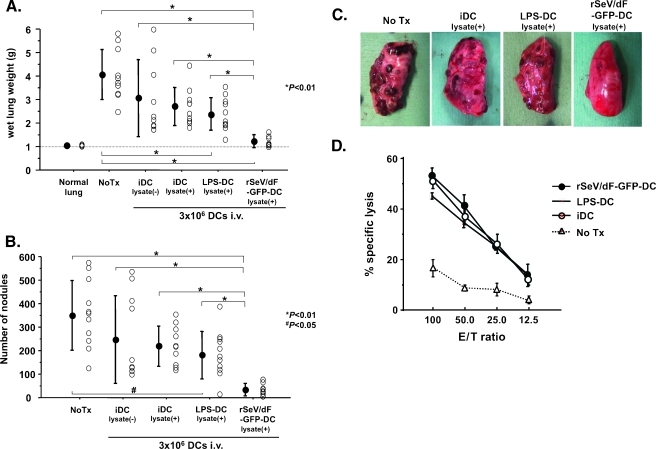
Figure 2.
Direct comparison of antimetastatic ability of iDC, LPS-DC, and rSeV/dF-GFP-DC on rat model of lung metastasis of AT6.3 prostate cancer. (A–C) Direct comparison of efficacy of iDC with or without tumor lysate pulsation (n = 10, respectively), LPS-DC with lysate (n = 11), and rSeV/dF-GFP-DC with lysate (n = 11): total wet lung weight (g) (A), number of metastatic nodules (B), and gross observation of left upper lobe (C). Normal lung, n = 6; and No Tx, n = 11. The treatment regimen was the same as that in panel A. All DCs were administered intravenously through the tail vein at 3 x 106 cells per vaccine. Note that the iDC group was included so as to exclude the effect of spontaneous activation through tumor antigen capture. *P < .01 and #P <.05. (D) CTL activity assessed in use of splenocytes. Each group contained n = 3.