Abstract
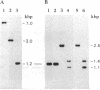
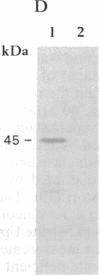
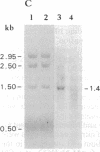
Nitrate-grown cells of Synechococcus PCC 7942 (Anacystis nidulans R2) contain a 45-kDa protein as a major protein in the cytoplasmic membrane but ammonium-grown cells lack it. A mutant (M45) was constructed by inactivating the gene encoding the 45-kDa protein. M45 did not grow under low concentrations of nitrate but high concentrations of nitrate could support its growth, with the optimal concentration being 40-70 mM. The growth rate of M45 was as high as that of the wild-type cells when ammonium was the nitrogen source. The 45-kDa protein was absent in M45 irrespective of the growth conditions. The activities of nitrate and nitrite reductases were higher in M45 than in wild type. The rate of nitrate-dependent O2 evolution in wild type measured in the presence of L-methionine D,L-sulfoximine and D,L-glyceraldehyde showed saturation kinetics with respect to nitrate concentration in the external medium. The nitrate concentration required to produce half the maximal rate was 1 μM. In M45, the rate of nitrate-dependent O2 evolution was nearly zero at nitrate concentrations <1 mM and was linearly increased as the concentration increased. The presumed absence of nitrate transport in M45 demonstrated by these results suggested that the 45-kDa protein is a nitrate transporter.
Keywords: cytoplasmic membrane, 45-kDa protein, in vitro mutagenesis, nitrate reductase, ammonium-grown cell
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bullerjahn G. S., Sherman L. A. Identification of a carotenoid-binding protein in the cytoplasmic membrane from the heterotrophic cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC6714. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):396–399. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.396-399.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden S. S., Brusslan J., Haselkorn R. Genetic engineering of the cyanobacterial chromosome. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:215–231. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53055-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrero A., Flores E., Guerrero M. G. Regulation of nitrate reductase levels in the cyanobacteria Anacystis nidulans, Anabaena sp. strain 7119, and Nostoc sp. strain 6719. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):175–180. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.175-180.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lara C., Romero J. M., Guerrero M. G. Regulated nitrate transport in the cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4376–4378. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4376-4378.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka A., Sugisaki H., Takanami M. Nucleotide sequence of the kanamycin resistance transposon Tn903. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 5;147(2):217–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90438-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omata T., Ogawa T. Biosynthesis of a 42-kD Polypeptide in the Cytoplasmic Membrane of the Cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans Strain R2 during Adaptation to Low CO(2) Concentration. Plant Physiol. 1986 Feb;80(2):525–530. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.2.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Kunisawa R., Mandel M., Cohen-Bazire G. Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (order Chroococcales). Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Jun;35(2):171–205. doi: 10.1128/br.35.2.171-205.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Szalay A. A. Stable integration of foreign DNA into the chromosome of the cyanobacterium Synechococcus R2. Gene. 1983 Sep;24(1):37–51. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90129-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]