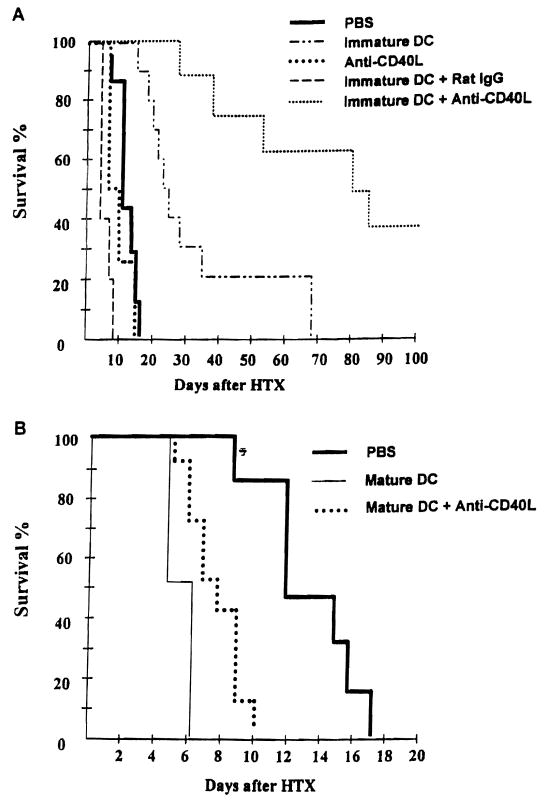
Figure 1.
A, Anti-CD40L mAb enhances the capacity of immature donor-derived DC to prolong vascularized cardiac allograft survival. Immature or mature DC were propagated from B10 (H-2b) mouse bone marrow, as described in Materials and Methods, and injected (2 × 106) i.v. either alone, or together with 200 μg anti-CD40L mAb, i.p. into C3H (H-2k) recipients, 7 days before B10 heart transplantation (HTX) on day 0. Control groups received either no treatment (PBS), anti-CD40L mAb, or normal rat IgG (isotype control) alone on day –7. B, Pretreatment with mature DC resulted in accelerated graft rejection, that was not reversed by mAb administration. Anti-CD40L mAb pretreatment alone did not significantly affect allograft survival. Results obtained from groups of 6–19 mice. Immature DC+anti-CD40L versus immature DC+ IgG, P<0.001; immature DC+anti-CD40L versus anti-CD40L, P<0.01; immature DC+anti-CD40L versus immature DC, P<0.01; immature DC versus PBS, P<0.01; mature DC versus PBS, P<0.01; mature DC+anti-CD40L versus PBS, P<0.05.