Figure 1.
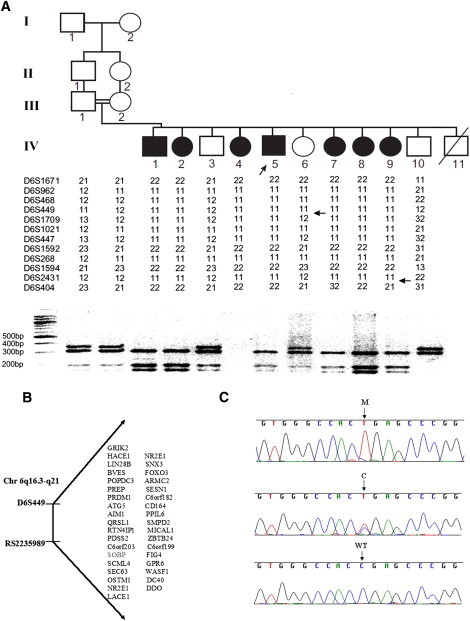
Gene Mapping and Mutation Identification
(A) Pedigree, haplotyping, and segregation of mutation in the family. The proband is indicated by an arrow. For mutation detection by restriction analysis, amplification of a 669 bp fragment from genomic DNA was performed with the use of primers A and B. The mutation introduces a Dde1 restriction site, which digests the 669 bp fragment into 310 bp, 195 bp, and164 bp fragments. The reaction products were separated by electrophoresis on 3% NuSieve/1% agarose gels.
(B) Candidate region on chromosome 6q16.3-q21, with the list of candidate genes.
(C) Sequence analysis in a patient, heterozygous carrier, and control individual. M, mutant allele; C, carrier; WT, homozygous wild-type. DNA from individual IV-4 was not available for mutation segregation analysis.
