Figure 2.
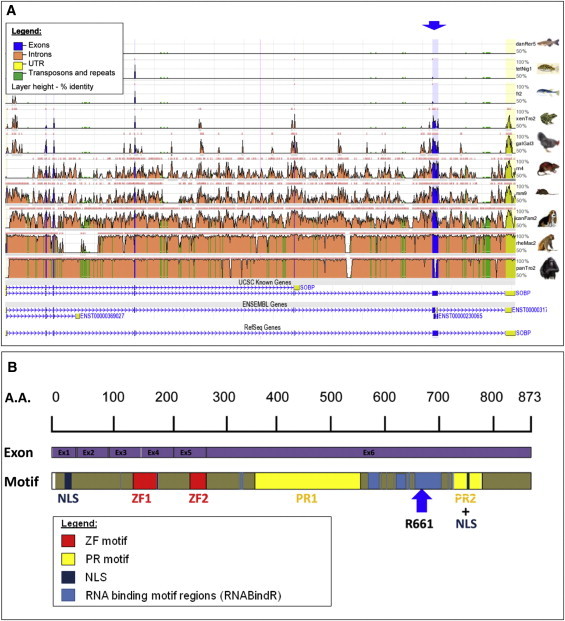
Bioinformatics Analysis of the Genomic Conservation of the SOBP and SOBP Domain and Motif Structure
(A) ECR browser analysis on human (hg18) was performed to show SOBP conservation between human and various species (danio, tetradon, fugu, Xenopus, gallus, rat, mouse, dog, rhesus, and chimp). Genomic conservation of exons (blue) and introns (orange), as well as the UTR (yellow) and repeats (green), is visualized. Layer height presents the percentage of identity (sequence conservation). Two different gene transcripts are shown at the bottom. The blue arrow shows a C>T change in nucleotide 1981 of exon 6 in SOBP.
(B) Domain properties for SOBP (A7XYQ1; SOBP_HUMAN) were obtained from UniProt. Two FCS-type zinc fingers (MYM-type zinc finger with FCS sequence motif, PF06467) and two proline-rich regions (IPR000694) are shown (red and yellow, respectively). NLS localization is also presented (navy). In addition, DNA and RNA binding motifs were predicted by the RNABindR server (light blue). The results from the BindN, PPRint, and MEME servers agree with those from the RNABindR server (data not shown). The blue arrow represents residue 661, in which the reported mutation occurred, causing truncation of SOBP.
