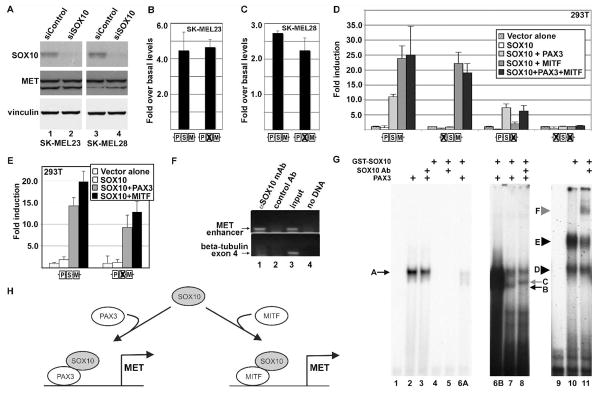
Figure 5.
SOX10 does not appear to directly activate the MET gene, but synergistically activates expression with either PAX3 or MITF. (A) Inhibition of SOX10 protein expression does not affect MET protein levels. Western analysis of cells transfected with either scrambled siRNA (lanes 1,3) or gene specific siRNA (lanes 2,4) show >90% reduction of SOX10 protein but no significant change in MET levels. (B,C) Alteration of a putative SOX site in the MET promoter does not alter reporter expression in SK-MEL23 (B) and SK-MEL28 (C) melanoma cells. (D) SOX10 does not activate the MET promoter in HEK-293T cells alone (white bars), but synergistically activates expression with either PAX3 (light grey) or MITF (dark grey). There is no significant increase in reporter expression when SOX10 is present with both PAX3 and MITF (black bars) than with MITF alone. Activation of the wild-type reporter construct (first bar set) with SOX10 alone is 0.9±0.7 fold over vector alone (white bar), 11.0±0.8 fold with PAX3 (light grey bar), 23.8±4.2 fold with MITF (grey bar), and 25.0±9.6 fold with both PAX3 and MITF (black bar). (E) Synergistic activation of the MET promoter reporter construct by SOX10 and PAX3 or MITF is unaffected when the putative SOX10 site is mutated. Reporter expression is not significantly reduced from wild-type reporter levels (bar set 1) when the putative SOX10 site shown in Figure 2 is mutated (bar set 2). For calculation of fold light units over basal promoter activity (y axis), luciferase activity is measured in arbitrary light units, normalized against beta-galactosidase activity, and divided by the measurements obtained for reporter vector alone. Each bar represents n=9, with standard error of the mean as shown. (F) SOX10 protein is located on the endogenous MET promoter in SK-MEL23 cells. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis utilized primers specific for the MET promoter region (top gels) or for exon 4 of the beta tubulin gene (bottom gels, negative control). Antibodies used for the immunoprecipitation are either against SOX10 (lane 1), or normal mouse IgG (control Ab, negative control lane 2). Input DNA was collected for each sample after cell sonication but before immunoprecipitation (positive control lane 3). The no DNA lanes lacked a template during PCR amplification (water only, negative control lane 4). (G) SOX10 does not directly bind to the enhancer, but is in complex with PAX3. Two probes were utilized for EMSA analysis, one containing the MET enhancer (lanes 1–8) or the P0 probe (SOX10 positive control, lanes 9–11). Lanes 1-6A are a short film exposure and lanes 6B-8 are a long exposure of the same gel. Lanes 6A and 6B are the same lane with different exposure times. Lane 1 is probe alone without the addition of PAX3 or SOX10 proteins. PAX3 binds to the MET enhancer and produces a slow migrating band (lane 2, arrow A) and this migration is not altered by the addition of SOX10 antibody (lane 3). SOX10 does not bind to the probe on its own (lane 4) or with SOX10 antibody (lane 5). PAX3 and SOX10 together results in a band migrating at the same level as PAX3 alone (arrow A) and an additional band (arrow B) with high levels (lane 6A,6B) or low levels (lane 7) of SOX10 protein. Addition of a SOX10-specific antibody alters the migration of this second band (lane 8, grey arrow C). A probe comprising sequence from the P0 promoter is utilized as a positve control for SOX10 binding (lanes 9–11). Lanes include probe without SOX10 protein (lane 9), or with SOX10 protein, resulting in two slow migrating bands (lane 10, arrowheads D and E). The addition of SOX10-specific antibody produces a slower migrating band (lane 11, grey arrowhead F). (H) Model for SOX10 synergistic activation of the MET promoter. SOX10 directly interacts with PAX3 or MITF, and this complex is recruited to an enhancer in the 5′ proximal MET promoter to drive gene expression.