Abstract
In the mononuclear title complex, [Co(NCS)2(C9H10N2O)2]·CH3OH, the cobalt(II) ion is surrounded by two (1-methyl-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methanol bidentate ligands and two thiocyanate ligands, and exhibits a distorted octahedral coordination by four N atoms and two O atoms. The structure is consolidated by hydrogen bonds between the organic ligand, thiocyanate anion and the uncoordinated methanol molecule, leading to a chain along [100].
Related literature
For the synthesis of the ligand, see: van Albada et al. (1995 ▶) and literature cited therein. For the cobalt(II) dithiocyanato adduct, see: Zeng et al. (2006 ▶). For the zinc(II) complex of a similar N-heterocycle, see: Zhou et al. (2007 ▶).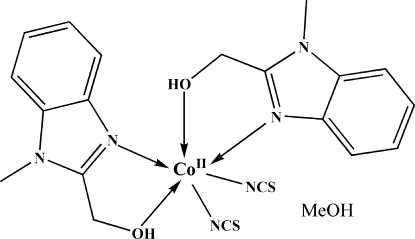
Experimental
Crystal data
[Co(NCS)2(C9H10N2O)2]·CH4O
M r = 531.53
Triclinic,

a = 7.5008 (13) Å
b = 10.3470 (18) Å
c = 16.042 (3) Å
α = 95.579 (3)°
β = 103.388 (3)°
γ = 95.179 (3)°
V = 1197.3 (4) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.93 mm−1
T = 173 K
0.40 × 0.36 × 0.09 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.708, T max = 0.921
8542 measured reflections
4146 independent reflections
3288 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.021
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.036
wR(F 2) = 0.116
S = 1.01
4146 reflections
298 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.39 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.26 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2001 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2001 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: X-SEED (Barbour, 2001 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810002114/si2239sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810002114/si2239Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Selected bond lengths (Å).
| Co1—N6 | 2.035 (3) |
| Co1—N5 | 2.047 (3) |
| Co1—N1 | 2.065 (3) |
| Co1—N3 | 2.079 (3) |
| Co1—O1 | 2.284 (2) |
| Co1—O2 | 2.327 (2) |
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2—H2A⋯O3 | 0.85 | 1.89 | 2.689 (3) | 155 |
| O3—H3A⋯S2i | 0.85 | 2.45 | 3.297 (3) | 179 |
| O1—H1⋯S1i | 0.85 | 2.36 | 3.177 (2) | 162 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
We thank Central South University and Guangxi Normal University for supporting this study.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The benzimidazol alcohols have widely been used as versatile ligands in coordination chemistry, and their metal complexes are of great interest in many fields. Recently, we have reported a few benzimidazol-2-yl methanol base cobalt and zinc complexes (Zeng et al. 2006, Zhou et al. 2007). In this paper, the title new cobalt(II) complex, (Fig. 1), is reported.
The complex consists of a mononuclear cobalt(II) complex molecule and a methanol molecule. The cobalt(II) ion is surrounded by two [(1-methyl-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methanol bidentate ligands and two thiocyanato ligands, and exhibits a distorted octahedral coordination by four N atoms and two O atoms (Albada et al. 1995) The coordinate bond lengths (Table 1) are typical and comparable to the corresponding values observed in our previously reported similar 2-Hydroxymethylbenzimidazole cobalt(II) complex (Zeng et al. 2006).
The structure is consolidated by hydrogen bonds between the organic ligand, thiocyanate anion and the uncoordinated methanol molecule, leading to a one-dimensional chain along the [100] direction. (Table 2, Fig. 2).
Experimental
(1-methyl-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl) methanol was purchased from a chemical supplier. This reagent (0.16 g, 1 mmol), cobalt(II) nitrate hexahydrate (0.15 g, 0.5 mmol) and ammonium thiocyanate(0.08 g, 1 mmol) were dissolved in water (10 ml) that was kept at about 333 K. Red platelets separated from the solution after two weeks.
Refinement
The C-bound H atoms were placed in calculated positions (C—H = 0.95–0.99 Å) and included in the refinement in the riding-model approximation, with Uiso(H) = 1.2(1.5)Ueq(C,Cmethyl). The hydroxy H atoms were located in a difference Fourier map and refined isotropically with distance restraints of O—H = 0.85 (1) Å, and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(O).
Figures
Fig. 1.
Anisotropic displacement ellipsoid plot of the [Co(II)(NCS)2(C9H10N2O)2] molecule at the 50% probability level; hydrogen atoms are drawn as sphere of arbitrary radius.
Fig. 2.
Part of the hydrogen bonded chains along [100] direction. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. Symmetry codes: (i) -1 + x, y, z.
Crystal data
| [Co(NCS)2(C9H10N2O)2]·CH4O | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 531.53 | F(000) = 550 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.474 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 7.5008 (13) Å | Cell parameters from 4367 reflections |
| b = 10.3470 (18) Å | θ = 2.8–25.0° |
| c = 16.042 (3) Å | µ = 0.93 mm−1 |
| α = 95.579 (3)° | T = 173 K |
| β = 103.388 (3)° | Plate, red |
| γ = 95.179 (3)° | 0.40 × 0.36 × 0.09 mm |
| V = 1197.3 (4) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer | 4146 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3288 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.021 |
| phi and ω scans | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 1.3° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −8→8 |
| Tmin = 0.708, Tmax = 0.921 | k = −12→12 |
| 8542 measured reflections | l = −19→19 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.036 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.116 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.01 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0643P)2 + 1.1088P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4146 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 298 parameters | Δρmax = 0.39 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.26 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. In Checkcif report, the following ALERTS were generatedPLAT230_ALERT_2_C Hirshfeld Test Diff for S1–C19.. 6.12 su PLAT230_ALERT_2_C Hirshfeld Test Diff for S2–C20.. 5.57 su PLAT232_ALERT_2_C Hirshfeld Test Diff (M—X) Co1–O1..5.19 su Author response: referring to the alert levels C, similar anisotropic displacement ellipsoids were observed in the solvent-free cobalt(II) complex (Zeng et al., 2006), and similar distances for S—C and Co—O (2.268 (2) Å) are found in Zeng et al. (2006). |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Co1 | 0.49422 (6) | 0.79547 (4) | 0.71477 (3) | 0.03196 (15) | |
| O1 | 0.3407 (3) | 0.9076 (2) | 0.61010 (13) | 0.0388 (5) | |
| H1 | 0.2553 | 0.9321 | 0.6326 | 0.058* | |
| O2 | 0.2200 (3) | 0.7225 (2) | 0.74875 (14) | 0.0420 (6) | |
| H2A | 0.2062 | 0.6429 | 0.7575 | 0.063* | |
| O3 | 0.0999 (4) | 0.4972 (2) | 0.79928 (16) | 0.0552 (7) | |
| H3A | 0.0496 | 0.5315 | 0.8370 | 0.083* | |
| N1 | 0.3872 (3) | 0.6541 (3) | 0.61074 (16) | 0.0321 (6) | |
| N2 | 0.2271 (4) | 0.5910 (3) | 0.47582 (16) | 0.0360 (6) | |
| N3 | 0.4426 (3) | 0.9434 (3) | 0.80037 (16) | 0.0335 (6) | |
| N4 | 0.3048 (4) | 1.0150 (3) | 0.90172 (17) | 0.0377 (6) | |
| N5 | 0.7251 (4) | 0.8800 (3) | 0.68486 (17) | 0.0402 (7) | |
| N6 | 0.6311 (4) | 0.6910 (3) | 0.80523 (19) | 0.0451 (7) | |
| C1 | 0.2850 (5) | 0.8331 (3) | 0.5273 (2) | 0.0435 (8) | |
| H1A | 0.3651 | 0.8629 | 0.4901 | 0.052* | |
| H1B | 0.1561 | 0.8449 | 0.4996 | 0.052* | |
| C2 | 0.2998 (4) | 0.6920 (3) | 0.53789 (19) | 0.0335 (7) | |
| C3 | 0.3678 (4) | 0.5184 (3) | 0.59742 (19) | 0.0321 (7) | |
| C4 | 0.4280 (4) | 0.4266 (3) | 0.6519 (2) | 0.0365 (7) | |
| H4A | 0.4974 | 0.4526 | 0.7096 | 0.044* | |
| C5 | 0.3834 (5) | 0.2958 (3) | 0.6193 (2) | 0.0447 (8) | |
| H5A | 0.4227 | 0.2310 | 0.6554 | 0.054* | |
| C6 | 0.2822 (5) | 0.2573 (4) | 0.5348 (2) | 0.0479 (9) | |
| H6B | 0.2539 | 0.1666 | 0.5148 | 0.057* | |
| C7 | 0.2218 (5) | 0.3459 (4) | 0.4795 (2) | 0.0430 (8) | |
| H7A | 0.1532 | 0.3190 | 0.4218 | 0.052* | |
| C8 | 0.2661 (4) | 0.4773 (3) | 0.51224 (19) | 0.0335 (7) | |
| C9 | 0.1212 (5) | 0.5970 (4) | 0.3872 (2) | 0.0444 (8) | |
| H9A | 0.1124 | 0.6885 | 0.3776 | 0.067* | |
| H9B | −0.0029 | 0.5510 | 0.3786 | 0.067* | |
| H9C | 0.1837 | 0.5554 | 0.3462 | 0.067* | |
| C10 | 0.1814 (5) | 0.7973 (3) | 0.8195 (2) | 0.0412 (8) | |
| H10A | 0.1972 | 0.7475 | 0.8698 | 0.049* | |
| H10B | 0.0525 | 0.8184 | 0.8045 | 0.049* | |
| C11 | 0.3106 (4) | 0.9185 (3) | 0.8402 (2) | 0.0348 (7) | |
| C12 | 0.5277 (4) | 1.0679 (3) | 0.83793 (19) | 0.0332 (7) | |
| C13 | 0.6722 (4) | 1.1464 (4) | 0.8213 (2) | 0.0427 (8) | |
| H13A | 0.7323 | 1.1183 | 0.7779 | 0.051* | |
| C14 | 0.7252 (5) | 1.2669 (4) | 0.8701 (2) | 0.0508 (9) | |
| H14A | 0.8219 | 1.3231 | 0.8589 | 0.061* | |
| C15 | 0.6418 (5) | 1.3092 (4) | 0.9354 (2) | 0.0506 (9) | |
| H15A | 0.6843 | 1.3923 | 0.9681 | 0.061* | |
| C16 | 0.4986 (5) | 1.2322 (4) | 0.9530 (2) | 0.0471 (9) | |
| H16A | 0.4411 | 1.2597 | 0.9975 | 0.056* | |
| C17 | 0.4430 (4) | 1.1128 (3) | 0.9026 (2) | 0.0373 (7) | |
| C18 | 0.1719 (5) | 1.0184 (4) | 0.9551 (2) | 0.0528 (10) | |
| H18A | 0.0893 | 0.9362 | 0.9418 | 0.079* | |
| H18B | 0.0995 | 1.0916 | 0.9433 | 0.079* | |
| H18C | 0.2377 | 1.0295 | 1.0162 | 0.079* | |
| C19 | 0.8474 (4) | 0.9482 (3) | 0.6751 (2) | 0.0354 (7) | |
| C20 | 0.7421 (4) | 0.6650 (3) | 0.8619 (2) | 0.0317 (7) | |
| C21 | 0.2200 (7) | 0.4131 (5) | 0.8363 (3) | 0.0730 (14) | |
| H21B | 0.3474 | 0.4535 | 0.8455 | 0.109* | |
| H21A | 0.2018 | 0.3309 | 0.7978 | 0.109* | |
| H21C | 0.1958 | 0.3952 | 0.8918 | 0.109* | |
| S2 | 0.89902 (12) | 0.63097 (9) | 0.94306 (5) | 0.0424 (2) | |
| S1 | 1.01807 (12) | 1.04930 (9) | 0.66347 (6) | 0.0445 (2) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Co1 | 0.0292 (2) | 0.0377 (3) | 0.0279 (2) | 0.00460 (18) | 0.00559 (17) | 0.00169 (18) |
| O1 | 0.0360 (12) | 0.0467 (13) | 0.0333 (12) | 0.0101 (10) | 0.0075 (10) | 0.0003 (10) |
| O2 | 0.0414 (13) | 0.0489 (14) | 0.0382 (13) | −0.0009 (11) | 0.0173 (11) | 0.0048 (11) |
| O3 | 0.0719 (18) | 0.0496 (15) | 0.0489 (15) | 0.0112 (14) | 0.0232 (14) | 0.0048 (12) |
| N1 | 0.0266 (13) | 0.0411 (15) | 0.0290 (14) | 0.0046 (11) | 0.0079 (11) | 0.0026 (11) |
| N2 | 0.0301 (14) | 0.0506 (17) | 0.0254 (13) | 0.0021 (12) | 0.0057 (11) | 0.0000 (12) |
| N3 | 0.0262 (13) | 0.0445 (16) | 0.0302 (14) | 0.0046 (11) | 0.0069 (11) | 0.0061 (12) |
| N4 | 0.0382 (15) | 0.0475 (17) | 0.0349 (14) | 0.0134 (13) | 0.0195 (12) | 0.0084 (12) |
| N5 | 0.0329 (15) | 0.0484 (17) | 0.0403 (16) | 0.0052 (13) | 0.0139 (13) | −0.0018 (13) |
| N6 | 0.0438 (17) | 0.0477 (18) | 0.0396 (16) | 0.0114 (14) | −0.0007 (14) | 0.0050 (13) |
| C1 | 0.044 (2) | 0.051 (2) | 0.0332 (18) | 0.0089 (16) | 0.0055 (15) | 0.0054 (15) |
| C2 | 0.0247 (15) | 0.0475 (19) | 0.0302 (16) | 0.0046 (13) | 0.0107 (13) | 0.0036 (14) |
| C3 | 0.0243 (15) | 0.0425 (18) | 0.0324 (16) | 0.0016 (13) | 0.0149 (13) | 0.0009 (14) |
| C4 | 0.0317 (17) | 0.0443 (19) | 0.0358 (17) | 0.0025 (14) | 0.0135 (14) | 0.0045 (15) |
| C5 | 0.045 (2) | 0.043 (2) | 0.052 (2) | 0.0053 (16) | 0.0233 (17) | 0.0076 (17) |
| C6 | 0.051 (2) | 0.040 (2) | 0.055 (2) | 0.0002 (17) | 0.0227 (18) | −0.0050 (17) |
| C7 | 0.0381 (19) | 0.056 (2) | 0.0343 (18) | −0.0029 (16) | 0.0159 (15) | −0.0067 (16) |
| C8 | 0.0266 (16) | 0.0448 (19) | 0.0313 (16) | 0.0016 (14) | 0.0145 (13) | −0.0001 (14) |
| C9 | 0.0383 (19) | 0.062 (2) | 0.0281 (17) | 0.0057 (17) | 0.0020 (14) | −0.0007 (16) |
| C10 | 0.0424 (19) | 0.045 (2) | 0.0438 (19) | 0.0089 (15) | 0.0213 (16) | 0.0116 (15) |
| C11 | 0.0297 (16) | 0.0445 (19) | 0.0340 (17) | 0.0094 (14) | 0.0107 (14) | 0.0120 (14) |
| C12 | 0.0272 (16) | 0.0422 (18) | 0.0291 (16) | 0.0095 (14) | 0.0029 (13) | 0.0037 (14) |
| C13 | 0.0296 (17) | 0.053 (2) | 0.0430 (19) | 0.0019 (15) | 0.0110 (15) | −0.0069 (16) |
| C14 | 0.0345 (19) | 0.058 (2) | 0.056 (2) | −0.0017 (17) | 0.0112 (17) | −0.0066 (19) |
| C15 | 0.041 (2) | 0.053 (2) | 0.051 (2) | 0.0014 (17) | 0.0065 (17) | −0.0123 (18) |
| C16 | 0.046 (2) | 0.059 (2) | 0.0378 (19) | 0.0163 (18) | 0.0111 (16) | −0.0029 (17) |
| C17 | 0.0311 (17) | 0.050 (2) | 0.0332 (17) | 0.0120 (15) | 0.0091 (14) | 0.0066 (15) |
| C18 | 0.057 (2) | 0.061 (2) | 0.054 (2) | 0.0158 (19) | 0.037 (2) | 0.0099 (19) |
| C19 | 0.0328 (18) | 0.0428 (19) | 0.0317 (17) | 0.0155 (15) | 0.0079 (14) | 0.0006 (14) |
| C20 | 0.0321 (17) | 0.0296 (16) | 0.0367 (17) | 0.0036 (13) | 0.0146 (15) | 0.0040 (13) |
| C21 | 0.084 (3) | 0.101 (4) | 0.056 (3) | 0.047 (3) | 0.039 (2) | 0.032 (3) |
| S2 | 0.0376 (5) | 0.0594 (6) | 0.0333 (4) | 0.0147 (4) | 0.0086 (4) | 0.0129 (4) |
| S1 | 0.0376 (5) | 0.0423 (5) | 0.0599 (6) | 0.0092 (4) | 0.0199 (4) | 0.0134 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Co1—N6 | 2.035 (3) | C5—C6 | 1.392 (5) |
| Co1—N5 | 2.047 (3) | C5—H5A | 0.9500 |
| Co1—N1 | 2.065 (3) | C6—C7 | 1.371 (5) |
| Co1—N3 | 2.079 (3) | C6—H6B | 0.9500 |
| Co1—O1 | 2.284 (2) | C7—C8 | 1.390 (5) |
| Co1—O2 | 2.327 (2) | C7—H7A | 0.9500 |
| O1—C1 | 1.421 (4) | C9—H9A | 0.9800 |
| O1—H1 | 0.8500 | C9—H9B | 0.9800 |
| O2—C10 | 1.411 (4) | C9—H9C | 0.9800 |
| O2—H2A | 0.8500 | C10—C11 | 1.474 (5) |
| O3—C21 | 1.384 (5) | C10—H10A | 0.9900 |
| O3—H3A | 0.8501 | C10—H10B | 0.9900 |
| N1—C2 | 1.315 (4) | C12—C13 | 1.387 (5) |
| N1—C3 | 1.389 (4) | C12—C17 | 1.401 (4) |
| N2—C2 | 1.351 (4) | C13—C14 | 1.380 (5) |
| N2—C8 | 1.388 (4) | C13—H13A | 0.9500 |
| N2—C9 | 1.470 (4) | C14—C15 | 1.392 (5) |
| N3—C11 | 1.317 (4) | C14—H14A | 0.9500 |
| N3—C12 | 1.397 (4) | C15—C16 | 1.378 (5) |
| N4—C11 | 1.345 (4) | C15—H15A | 0.9500 |
| N4—C17 | 1.378 (4) | C16—C17 | 1.382 (5) |
| N4—C18 | 1.457 (4) | C16—H16A | 0.9500 |
| N5—C19 | 1.155 (4) | C18—H18A | 0.9800 |
| N6—C20 | 1.154 (4) | C18—H18B | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.498 (5) | C18—H18C | 0.9800 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9900 | C19—S1 | 1.636 (4) |
| C1—H1B | 0.9900 | C20—S2 | 1.630 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.388 (5) | C21—H21B | 0.9800 |
| C3—C8 | 1.405 (4) | C21—H21A | 0.9800 |
| C4—C5 | 1.384 (5) | C21—H21C | 0.9800 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9500 | ||
| N6—Co1—N5 | 95.76 (12) | C7—C6—H6B | 118.9 |
| N6—Co1—N1 | 102.52 (11) | C5—C6—H6B | 118.9 |
| N5—Co1—N1 | 102.62 (10) | C6—C7—C8 | 116.5 (3) |
| N6—Co1—N3 | 96.87 (11) | C6—C7—H7A | 121.7 |
| N5—Co1—N3 | 101.37 (10) | C8—C7—H7A | 121.7 |
| N1—Co1—N3 | 147.26 (10) | N2—C8—C7 | 132.0 (3) |
| N6—Co1—O1 | 178.26 (10) | N2—C8—C3 | 105.7 (3) |
| N5—Co1—O1 | 84.12 (10) | C7—C8—C3 | 122.2 (3) |
| N1—Co1—O1 | 75.83 (9) | N2—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| N3—Co1—O1 | 84.85 (9) | N2—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| N6—Co1—O2 | 88.91 (11) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| N5—Co1—O2 | 173.52 (10) | N2—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| N1—Co1—O2 | 80.65 (9) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| N3—Co1—O2 | 73.54 (9) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| O1—Co1—O2 | 91.34 (8) | O2—C10—C11 | 107.8 (3) |
| C1—O1—Co1 | 113.38 (19) | O2—C10—H10A | 110.1 |
| C1—O1—H1 | 116.7 | C11—C10—H10A | 110.1 |
| Co1—O1—H1 | 100.9 | O2—C10—H10B | 110.1 |
| C10—O2—Co1 | 114.71 (19) | C11—C10—H10B | 110.1 |
| C10—O2—H2A | 106.8 | H10A—C10—H10B | 108.5 |
| Co1—O2—H2A | 116.5 | N3—C11—N4 | 113.3 (3) |
| C21—O3—H3A | 109.5 | N3—C11—C10 | 123.5 (3) |
| C2—N1—C3 | 106.1 (3) | N4—C11—C10 | 123.2 (3) |
| C2—N1—Co1 | 117.9 (2) | C13—C12—N3 | 131.3 (3) |
| C3—N1—Co1 | 135.7 (2) | C13—C12—C17 | 119.5 (3) |
| C2—N2—C8 | 106.9 (3) | N3—C12—C17 | 109.2 (3) |
| C2—N2—C9 | 127.6 (3) | C14—C13—C12 | 117.4 (3) |
| C8—N2—C9 | 125.5 (3) | C14—C13—H13A | 121.3 |
| C11—N3—C12 | 104.8 (3) | C12—C13—H13A | 121.3 |
| C11—N3—Co1 | 118.5 (2) | C13—C14—C15 | 122.4 (4) |
| C12—N3—Co1 | 136.2 (2) | C13—C14—H14A | 118.8 |
| C11—N4—C17 | 107.4 (3) | C15—C14—H14A | 118.8 |
| C11—N4—C18 | 126.4 (3) | C16—C15—C14 | 121.0 (3) |
| C17—N4—C18 | 126.2 (3) | C16—C15—H15A | 119.5 |
| C19—N5—Co1 | 167.6 (3) | C14—C15—H15A | 119.5 |
| C20—N6—Co1 | 160.2 (3) | C15—C16—C17 | 116.6 (3) |
| O1—C1—C2 | 108.7 (3) | C15—C16—H16A | 121.7 |
| O1—C1—H1A | 110.0 | C17—C16—H16A | 121.7 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 110.0 | N4—C17—C16 | 131.6 (3) |
| O1—C1—H1B | 110.0 | N4—C17—C12 | 105.3 (3) |
| C2—C1—H1B | 110.0 | C16—C17—C12 | 123.2 (3) |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 108.3 | N4—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| N1—C2—N2 | 112.9 (3) | N4—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| N1—C2—C1 | 122.2 (3) | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| N2—C2—C1 | 124.9 (3) | N4—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—N1 | 131.5 (3) | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C8 | 120.0 (3) | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| N1—C3—C8 | 108.5 (3) | N5—C19—S1 | 177.8 (3) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 117.7 (3) | N6—C20—S2 | 178.9 (3) |
| C5—C4—H4A | 121.2 | O3—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 121.2 | O3—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.3 (3) | H21B—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 119.3 | O3—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 119.3 | H21B—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 122.2 (3) | H21A—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2—H2A···O3 | 0.85 | 1.89 | 2.689 (3) | 155 |
| O3—H3A···S2i | 0.85 | 2.45 | 3.297 (3) | 179 |
| O1—H1···S1i | 0.85 | 2.36 | 3.177 (2) | 162 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1, y, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SI2239).
References
- Albada, G. A. van, Lakin, M. T., Veldman, N., Spek, A. L. & Reedijk, J. (1995). Inorg Chem 34, 4910–4917.
- Barbour, L. J. (2001). J Supramol Chem 1, 189–191.
- Bruker (2001). SAINT and SMART Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Goöttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). publCIF. In preparation.
- Zeng, M.-H., Zhou, Y.-L. & Ng, S. W. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, m2101–m2102.
- Zhou, Y.-L., Zeng, M.-H. & Ng, S. W. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, m15–m16.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810002114/si2239sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810002114/si2239Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




