Figure 3.
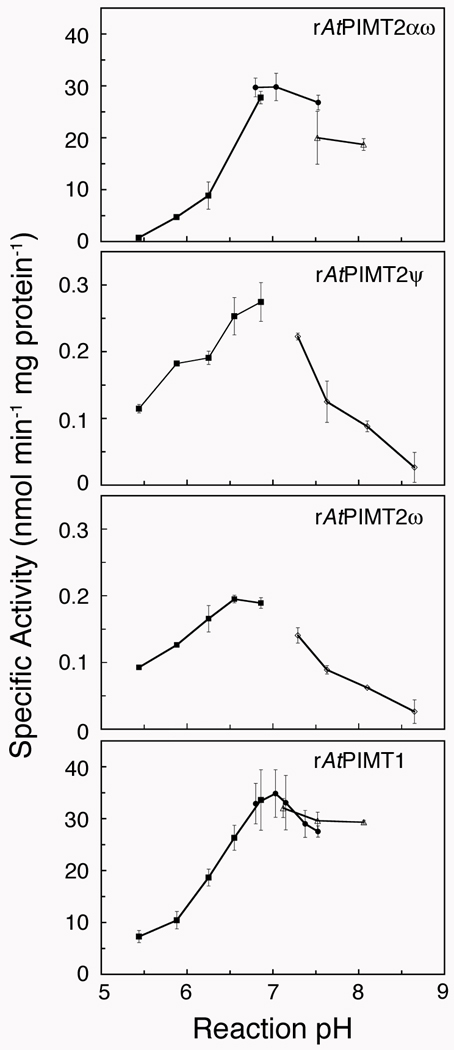
The effect of pH on the activity of recombinant Arabidopsis L-isoAsp methyltransferases. Methyltransferase activity at different pH reaction conditions was assayed as described under “Materials and Methods” with rAtPIMT2αω (120 ng protein), rAtPIMT2ψ (1.7 µg protein), rAtPIMT2ω (1.6 µg protein), and rAtPIMT1 (70 ng protein) at 40 °C for 10 min. In preliminary trials, the pHs of reactions at 40 °C were measured after dilution of each buffer, and each buffer was then used to adjust the reaction pH. The citrate-phosphate buffer (■; reaction pHs 5.4 to 7.0) was a 1 M citric acid solution mixed with 2 M sodium dibasic phosphate and diluted 5-fold into the final assay mixture. Additionally, 1 M buffer solutions of sodium phosphate (●; reaction pHs 6.9 to 7.6), HEPES (△; reaction pHs 7.1 to 8.1), and Tris-HCl (◊; reaction pHs 7.4 to 8.9) were diluted to a final concentration of 200 mM. The rAtPIMT2ψ and rAtPIMT2ω isozymes were purified in parallel and assayed in at least duplicate, as were rAtPIMT2αω and rAtPIMT1 except at a later date. Error bars represent the standard deviation from the mean.
