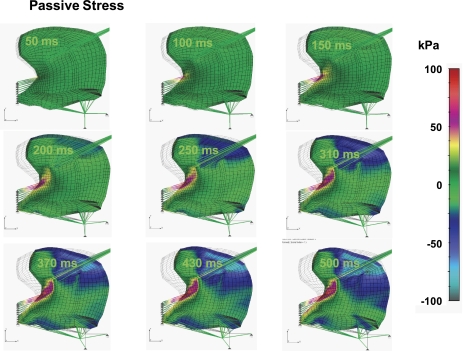
Fig. 7.
Simulated passive stress field during swallowing. Passive stress is defined by Eq. 12 and represents the stress in the parallel elastic element, σξξE, in direction of muscle fiber ξ. The color code represents the magnitude of σξξE in kilopascals. σE is the passive stress tensor, and σξξE is the most relevant component of this tensor. These results demonstrate that, within the current two-dimensional framework, passive stress tends to align with active stress in the apparent distribution of the superior regions of the genioglossus. The passive stress in both the longitudinal and the transverse directions considers only the passive elasticity and does not account for the increase of stiffness during contraction caused by bound cross bridges.