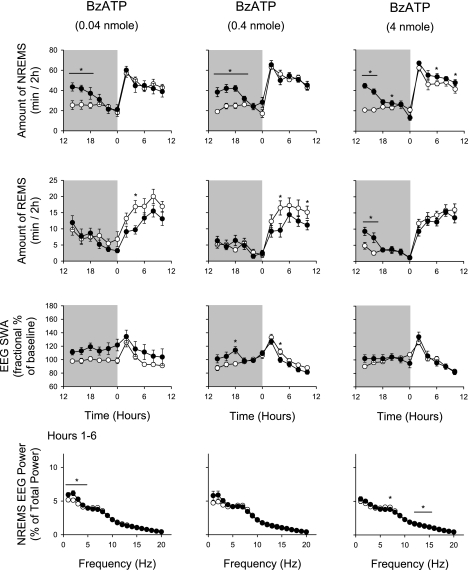
Fig. 1.
Nighttime (shaded area) injection of 2′(3′)-O-(4-benzoylbenzoyl)adenosine 5′-triphosphate (BzATP) enhanced non-rapid eye movement sleep (NREMS). Rats received 1 of 3 doses of BzATP as indicated at dark onset. All 3 doses enhanced duration of NREMS during the initial 6–8 h after injection. The highest dose also enhanced duration of NREMS in the subsequent light period. BzATP inhibited duration of rapid eye movement sleep (REMS) during the daylight period occurring 12 h after the injection after the lower 2 doses. After the highest dose, REMS was enhanced during the first 4 h after injection. BzATP induced enhancement of electroencephalographic slow-wave activity (EEG SWA). BzATP at the lowest dose enhanced EEG delta power; this effect was absent after the higher doses. EEG power values were obtained during the first 6 h after injection. ○, Control values; ●, values obtained after BzATP injections. *Significant differences between control and test days (P < 0.05, paired t-test).