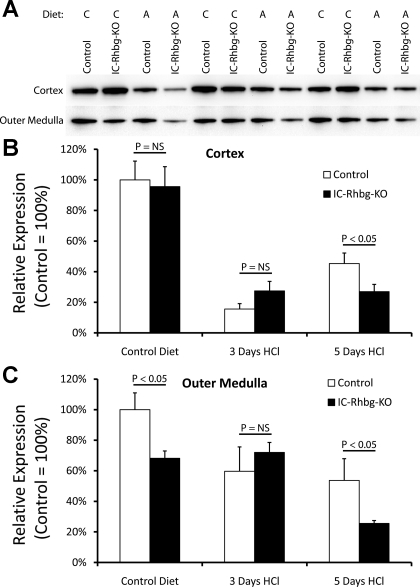
Fig. 7.
Effect of IC-Rhbg-KO and acid loading on glutamine synthetase expression. A: glutamine synthetase expression by immunoblot analyses in the cortex and outer medulla of IC-Rhbg-KO and C mice. Diet is either control (C) or acid (A). B: quantified data. In the cortex, IC-Rhbg-KO did not alter glutamine synthetase expression on control diet. Metabolic acidosis decreased glutamine synthetase expression in the cortex in both C and IC-Rhbg-KO mice. After 3 days of acid loading, there was no difference in glutamine synthetase expression between C and IC-Rhbg-KO mice. However, after 5 days of acid loading, glutamine synthetase expression was decreased significantly more in IC-Rhbg-KO mice than in C mice. C: changes in glutamine synthetase expression in the outer medulla in response to IC-Rhbg-KO and to acid loading. Under basal conditions, glutamine synthetase expression was significantly less in IC-Rhbg-KO than in C mice. Acid loading decreased glutamine synthetase expression. After 3 days of acid loading, glutamine synthetase expression did not differ significantly in the outer medulla between C and IC-Rhbg-KO mice. However, after 5 days of acid loading, glutamine synthetase expression was decreased significantly more in IC-Rhbg-KO than in C mice.