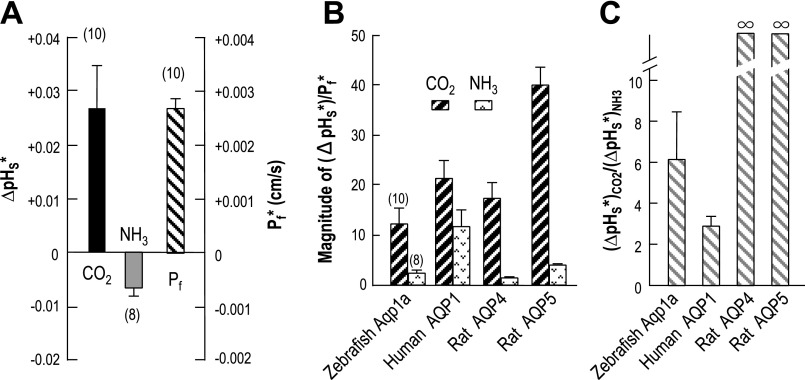
Fig. 10.
Indices of the CO2 and NH3 permeability of Aqp1a. A: indices of the Aqp1a-dependent CO2 and NH3 permeability (ΔpHS*) and the Aqp1a-dependent (Pf*). The leftmost bar of CO2 is an index of the Aqp1a-dependent CO2 permeability. We subtracted the mean value of ΔpHS induced by CO2 in day-matched, H2O-injected control oocytes (data contributing to the H2O bar for Fig. 8A) from the ΔpHS induced by CO2 in individual oocytes expressing Aqp1a (data contributing to the Aqp1a bar for Fig. 8A). Similarly, the middle bar of NH3 is an index of the Aqp1a-dependent NH3 permeability, and the rightmost bar of Pf is the Aqp1a-dependent osmotic water permeability (Pf*). B: Aqp1a-dependent parameters normalized to Pf*. The leftmost hatched bar of Aqp1a is the result of dividing the Aqp1a-dependent index of CO2 permeability of individual oocytes (data contributing to the bar for CO2 in A) by the corresponding Aqp1a-dependent Pf values of the same oocytes (data contributing to the bar for Pf in A). The rightmost stippled bar is the result of a similar manipulation, but starting with the Aqp1a-dependent index of NH3 permeability of individual oocytes (data contributing to the bar for NH3 in A). The other three pairs of bars represent data reported in a previous study (30) on human AQP1, rat AQP4, and rat AQP5. C: ratio of Aqp1a-dependent indices of CO2 and NH3 permeability. The bar for Aqp1a is the result of dividing the Aqp1a-dependent index of CO2 permeability of individual oocytes (data contributing to the bar for CO2 in A) by the corresponding index of NH3 permeability of the same oocytes (data contributing to the bar for NH3 in A). The bars for human AQP1, rat AQP4, and rat AQP5 represent data reported in a previous study (30).