Figure 3.
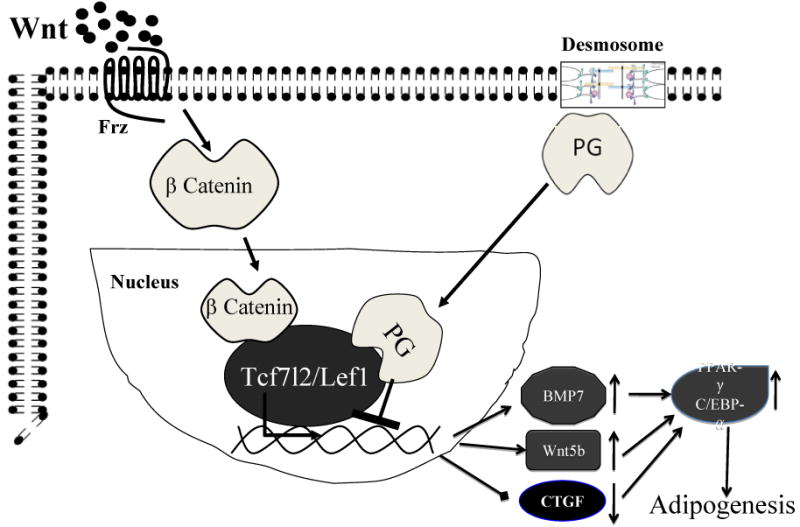
Pathogenesis of ARVC. Mutations in desmosomal proteins interfere with efficient and proper assembly of desmosomes, which allows the plakoglobin (PG) to translocate from desmosomes to the nucleus. In the nucleus, PG interferes with proper assembly of the Wnt canonical signaling protein complex and suppresses gene expression through the β-catenin/Lef7l2 transcriptional assembly.
The net effect is removal of the inhibitory effects of the canonical Wnt signaling and hence increased expression of bone morphogenic protein 7 (BMP7) and noncanonical Wnt5b, which are known promoters of adipogenesis. Likewise, suppression of the canonical Wnt signaling reduces expression of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), which is a known inhibitor of adipogenesis. The transcriptional switch from myogenesis to adipogenesis promotes the differentiation of a subset of second heart field progenitor cells to adipocytes.
