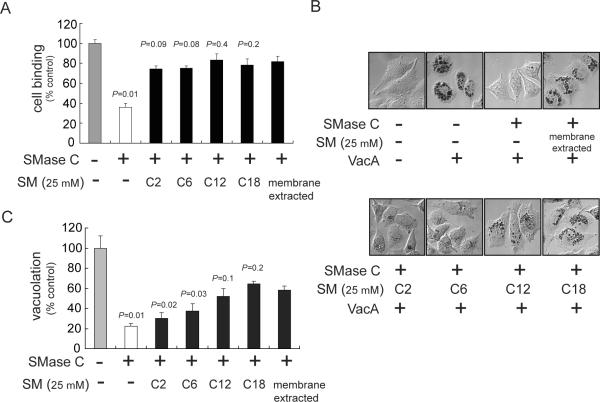
Fig. 2.
Effects of SM acyl chain length on cell binding and sensitivity to VacA.
AZ-521 cells were incubated with SMase C (50 mU/mL) for 1 h at 37 °C, and then chilled on ice to 0 °C. The cells were washed with ice-cold complete cell medium to remove SMase C. The cells were then incubated for 30 min on ice in the absence or presence of pre-chilled C2-SM, C6-SM, C12-SM, C18-SM, or membrane extracted SM (all at 25 μM). The cells were further incubated with prechilled Alexa Fluor 488-labeled VacA (50 nM) (A) or unlabeled VacA (50 nM) (B,C). After 1 h, the cells were analyzed for VacA binding (A) or further incubated at 37 °C and under 5% CO2 (B,C).
A. The level of VacA binding was determined using flow cytometry. Cell binding was calculated by determining the geometric mean fluorescence intensities of each sample. The results shown were derived from data combined from three independent experiments in which binding was normalized to control cells that had been mock-pretreated with complete cell medium prior to VacA binding. Statistical significance was calculated for differences in VacA binding between those cells pretreated sequentially with SMase C alone or SMase C and acyl chain variants of SM, and, those cells pretreated with SMase C and then “membrane extracted” SM.
B. After 8 h, the cells were stained with neutral red and visualized using DIC microscopy.
C. Cellular vacuolation was quantified using the neutral red assay. The results shown were derived by normalizing neutral red uptake to that measured in control cells that had been mock-pretreated with complete cell medium prior to VacA binding. Statistical significance was calculated for differences in vacuolation between those cells pretreated sequentially with SMase C alone or SMase C and acyl chain variants of SM, and, those cells pretreated with SMase C and then “membrane extracted” SM.