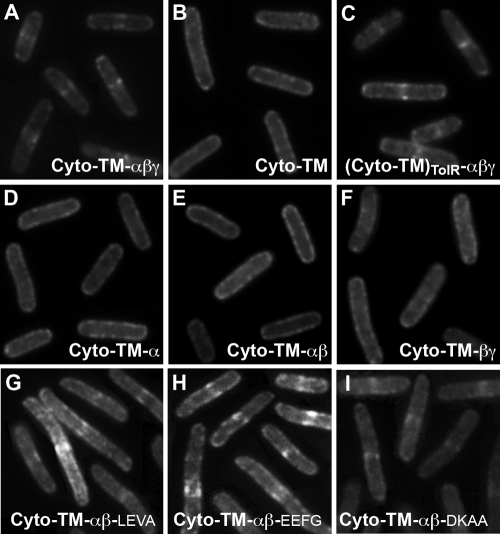
FIG. 2.
Fluorescence micrographs resulting from heterologous septal targeting experiments in E. coli in which the prey was GFP-PBP 2B and the bait was E. coli ZapA fused to either full-length DivIB (A) or one of the following: the Cyto-TM region only of DivIB (B), the entire extracytoplasmic region of B. subtilis DivIB fused to the Cyto-TM region of E. coli TolR (C), a truncated version of DivIB missing the C-terminal β domain and γ tail (D), a truncated version of DivIB missing the C-terminal γ tail (E), or a DivIB mutant in which the extracytoplasmic α domain has been excised (F). Panels G to I show the GFP-PBP 2B localization patterns obtained when the β domain in the Cyto-TM-αβ construct was extended by 16 residues (Cyto-TM-αβ-LEVA), 23 residues (Cyto-TM-αβ-EEFG), or 29 residues (Cyto-TM-αβ-DKAA). Septal localization of GFP-PBP 2B in panels A and C and G to I is indicated by fluorescent stripes or dots at midcell.