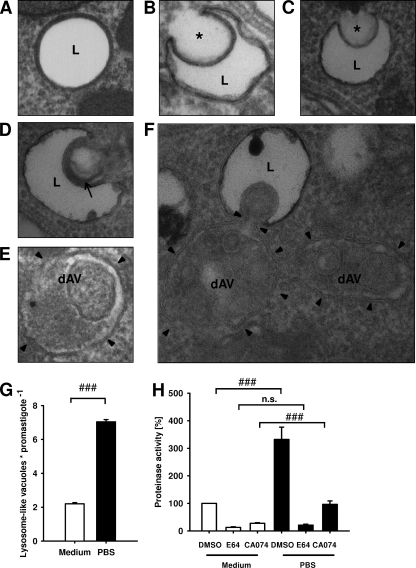
FIG. 7.
Characterization of lysosome-like vacuoles. (A to F) Stationary-phase promastigotes harvested directly from blood agar plates (A to E) or further starved in PBS (F) were investigated by transmission electron microscopy. Asterisks, microautophagy-like invaginations of membranes of lysosome-like vacuoles; arrow, a macroautophagic-like multiple-layered membranous structure fusing with lysosome-like vacuole; arrowheads, membrane bordering dAVs; L, lysosome-like vacuoles. (G) The numbers of lysosome-like vacuoles were determined by transmission electron microscopy in saggital sections of promastigotes incubated for 24 h in nutrient-rich medium or starved for 24 h in PBS (n = 25 saggital sections). (H) E64- and CA074-sensitive cysteine cathepsin activities detected by fluorescence protease activity assay in promastigotes cultured for 24 h in medium or starved for 24 h in PBS. For fluorescence proteinase activity assays, protein lysates that had been obtained from medium- and PBS-cultured promastigotes were incubated with DMSO, 100 μM E64, or 100 μM CA074. Proteinase activities were determined by proteolytic degradation of the fluoropeptide Z-Phe-Arg-AMC. The protease activity in DMSO-incubated lysates obtained from medium-cultured promastigotes was set equal to 100%. Values represent means ± SEMs for four independent experiments. ###, P ≤ 0.001; n.s., not significant.