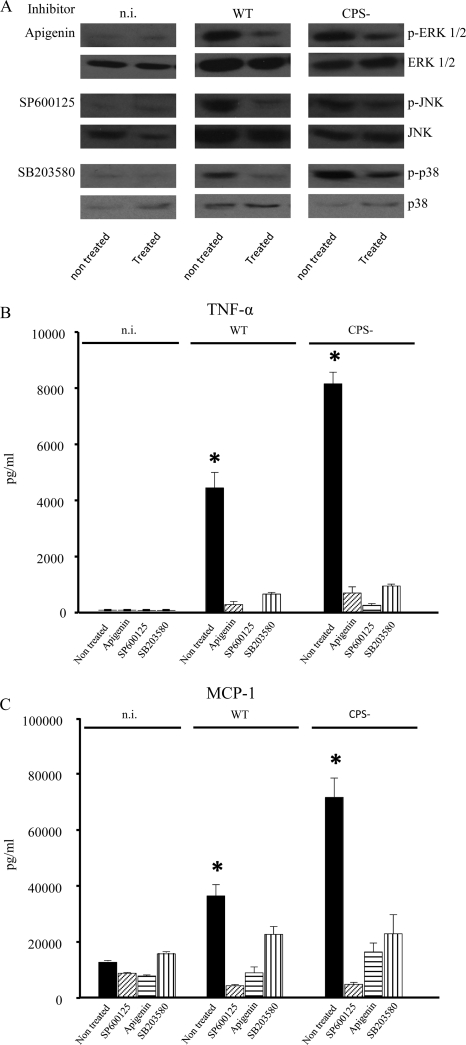
FIG. 8.
Pharmacologic inhibition of MAPKs. Murine microglial cells were treated with various inhibitors 1 h prior to infection with the S. suis WT strain or its CPS− mutant (1 × 106 bacteria). Apigenin (50 μM), SP600125 (50 μM), and SB203580 (75 μM) inhibit ERK 1/2, JNK, and p38, respectively. The inhibitors were all used at maximal subcytotoxic doses for a total of 13 h. (A) To confirm inhibition of MAPK phosphorylation, cell extracts were recovered after 2 h (p-ERK and p-JNK) or 4 h (p-p38) of bacterium-cell contact and then analyzed by Western blotting using specific antibodies for each of the proteins tested. The results are representative of three independent experiments. (B and C) To evidence inhibition in cytokine production, cells were infected for 12 h, and the supernatant was recovered for detection of TNF-α (B) and MCP-1 (C) production by ELISA. The data are expressed as means plus SEM from three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05, indicating significant differences from cells treated with MAPK inhibitors.