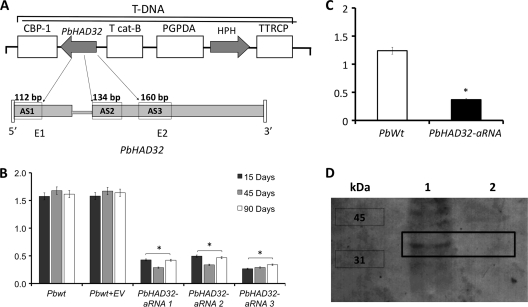
FIG. 2.
Generation of P. brasiliensis PbHAD32 aRNA strains. (A) T-DNA construct for aRNA silencing of PbHAD32 in P. brasiliensis via ATMT. PbHAD32 aRNA oligonucleotides AS1 (base pairs 1 to 112 of PbHAD32; exon 1), AS2 (base pairs 175 to 309 of PbHAD32; exon 2), and AS3 (base pairs 376 to 536 of PbHAD32; exon 2) were amplified, individually placed under the control of the calcium-binding protein (CBP1) promoter, and later on inserted into the T-DNA of the binary vector pUR5750 for ATMT of P. brasiliensis. (B) Gene expression levels of PbHAD32 in PbWt, PbWt transformed with the empty vector (PbWt + EV), and PbHAD32 aRNA yeast cells after subculture for 15, 45, and 90 days (gene expression levels obtained by RT-PCR were normalized to the level of expression of the internal reference, TUB2; *, P < 0.05 compared with PbWt and PbWt transformed with the empty vector). (C) Gene expression levels of PbHAD32 in PbWt and PbHAD32 aRNA yeast cells after the yeast-to-mycelium transition (Y-M), production of conidia (M-C), and transition into yeast cells (C-Y) (the complete process was Y-M-C-Y) (gene expression levels obtained by RT-PCR were normalized to the level of expression of the internal reference, TUB2; *, P < 0.05 compared with PbWt). (D) Western blot analysis of total protein extracts from PbHAD32 in PbWt and PbHAD32 aRNA yeast cells. Lane 1, PbWt; lane 2, PbHAD32 aRNA.