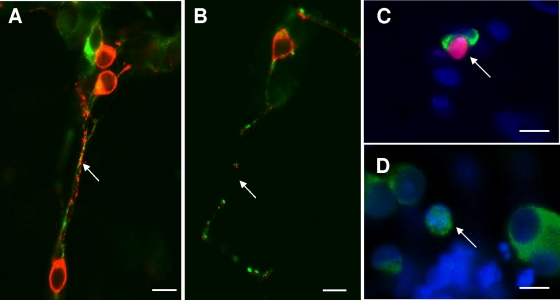
FIG. 3.
Onset of neurodegeneration in enteric neuronal cocultures exposed to secreted components from E. histolytica (Eh-SEC) for 4 h. (A and B) Higher-magnification view of control (A) and Eh-SEC-treated (B) cocultures showing coexpression of SNAP-25 (red) and the axon-specific intermediate filament βIII-tubulin (green) in axons. Both antibodies reveal prominent breaks in axon structure after treatment with Eh-SEC. Scale bar, 20 μm. (C) Example of uptake of the vital stain propidium iodide (red) at 4 h of treatment with Eh-SEC (30 μg/ml), indicating loss of viability. Cultures were subsequently labeled with anti-HuD antibodies (green) to identify neurons and the pan-nuclear fluorochrome Hoechst 333242 (blue) to identify all nuclei in the field. Scale bar, 20 μm. (D) Degenerating neuron identified with anti-HuD immunocytochemistry (green; arrow) and nuclear staining with Hoechst 33342 (blue), showing a condensed neuron with nuclear HuD labeling. Scale bar, 20 μm.