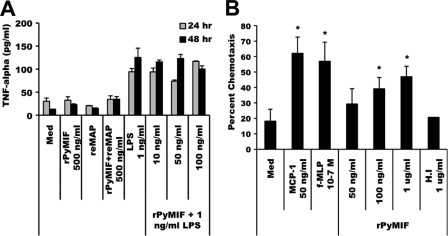
FIG. 3.
Functional activity of rPyMIF. (A) TNF-α release. Thioglycolate-elicited peritoneal macrophages (1 × 105 cells/well) were cultured in the presence of LPS alone (1 ng/ml), rPyMIF alone (500 ng/ml), or LPS (1 ng/ml) plus increasing concentrations of rPyMIF (10 to 100 ng/ml). In control experiments, rPyMIF was pretreated with recombinant methionine amino peptidase (reMAP) to remove the N-terminal methionine residue. Culture supernatants were harvested after 24 h or 48 h, and the TNF-α concentration was measured by ELISA. Basal levels of TNF-α release were determined from cells cultured in medium (Med) alone. (B) Chemotaxis. Murine peritoneal macrophages (1 × 105 to 2 × 105 cells/well) were loaded into the top well of a transwell chamber, and increasing concentrations of rPyMIF were loaded into the lower chambers. The migration of macrophages across the transwell membrane after a 3-h incubation was quantitated and expressed as percent chemotaxis. MCP-1 and f-MLP served as positive controls. Heat-inactivated (H.I) rPyMIF and medium alone were used as negative controls. An asterisk indicates significant differences in values (P < 0.05) relative to those of medium alone.