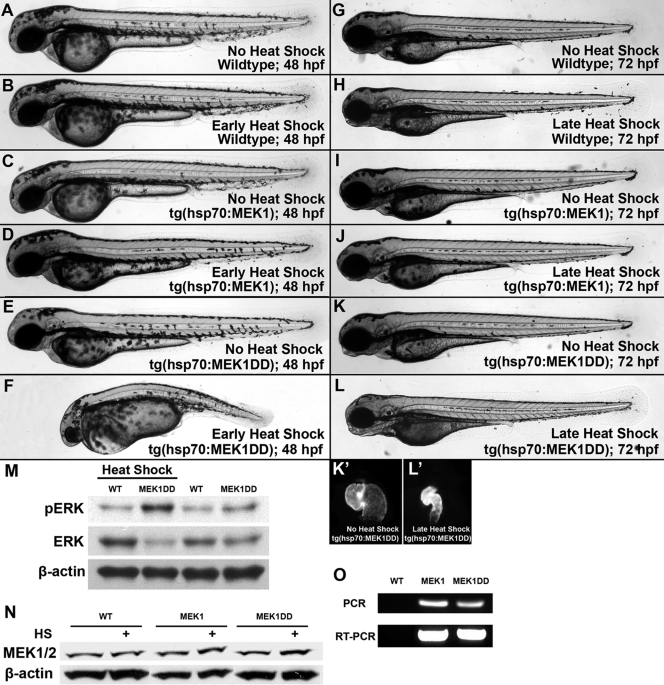
FIG. 4.
Phenotypes in inducible transgenic lines are consistent with global activation. Transgenic F1 embryos expressing activated or wild-type MEK1 under the control of a heat shock protein promoter were generated from our mosaic founders. Wild-type and tg(hsp70:MEK1) embryos had no obvious phenotype after heat shock (A to D), and tg(hsp70:MEK1DD) embryos showed defects 24 h following induction from 6 to 7 hpf (F). Uninduced tg(hsp70:MEK1DD) embryos appeared normal (E). Milder effects were noted in approximately 25% of embryos expressing MEK1DD (n, 124), when heat shock induction was performed from 47 to 48 hpf, and again from 52 to 53 hpf (K and L). Obvious effects were limited to the heart, which had a smaller size and impaired function compared to those of uninduced controls (K′ and L′). These heart effects could be visualized due to the CMLC2-driven GFP expression incorporated into our transgenic constructs. Wild-type and tg(hsp70:MEK1) embryos had no obvious defects following late heat shock induction (H and J). (M and O) pERK1/2 levels increased in tg(hsp70:MEK1DD) but not tg(hsp70:MEK1) or sibling embryos 1 h after induction (M), and genomic incorporation and expression of each transgene were verified by PCR and RT-PCR, respectively (O). (N) Heat shock induction for 2 h mildly increased MEK1 protein levels in both heat shock-regulated lines: hsp70:MEK1 and hsp70:MEK1DD.