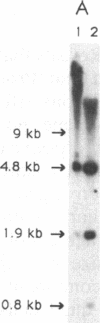
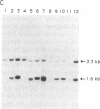
Abstract
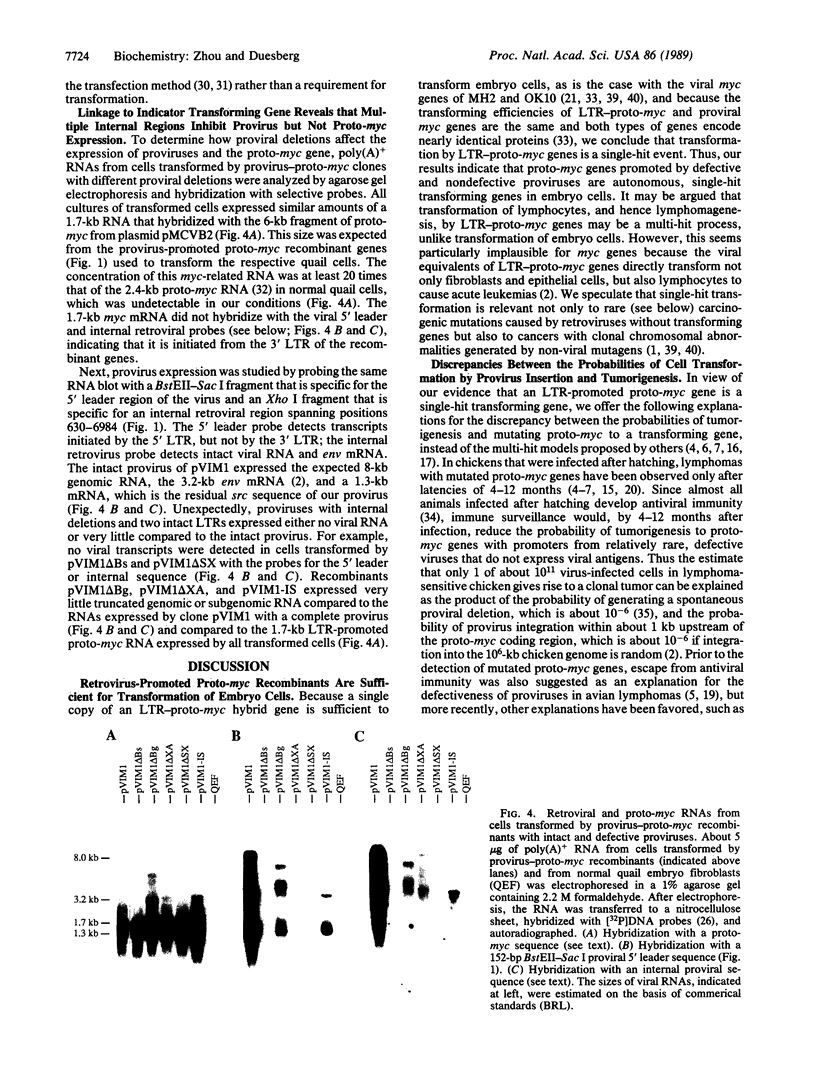
Lymphomas of certain strains of chickens infected by retroviruses frequently contain recombinant transforming genes in which the promoter of the cellular proto-myc gene is replaced by that of a defective rather than an intact retrovirus. Here we ask whether the resulting hybrid genes are sufficient for tumorigenic transformation like viral myc genes. Further, we ask whether retroviruses must be defective in order to mutate proto-myc to a transforming gene or whether the defectiveness plays a transformation-independent function in tumorigenesis. For this purpose the defective provirus of proviral-proto-myc recombinants from lymphomas were repaired, or intact proviruses were recombined with proto-myc genes in vitro, and then compared to recombinant proto-myc genes with defective proviruses for transforming function in quail embryo fibroblasts. It was found that a single copy of a provirus-proto-myc recombinant gene with an intact provirus is sufficient to transform a quail embryo cell in vitro. Moreover, our analyses showed that multiple internal retroviral deletions [corrected] eliminate or inhibit provirus expression. The effect of these deletions [corrected] was detectable only because the inactive proviruses were linked to the selectable, transforming proto-myc gene marker. It is consistent with our results that proviral defectiveness of recombinant proto-myc genes is necessary in vivo for the clonal growth of a transformed cell into a tumor to escape antiviral immunity. The large discrepancy between the probabilities of provirus insertion and tumorigenesis is suggested to reflect the low probabilities of spontaneous deletion of the provirus and of rare, strain-specific defects of tumor-resistance genes of the host.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrigo S., Yun M., Beemon K. cis-acting regulatory elements within gag genes of avian retroviruses. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):388–397. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba T. W., Humphries E. H. Formation of a transformed follicle is necessary but not sufficient for development of an avian leukosis virus-induced lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):213–216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacon L. D., Witter R. L., Crittenden L. B., Fadly A., Motta J. B-haplotype influence on Marek's disease, Rous sarcoma, and lymphoid leukosis virus-induced tumors in chickens. Poult Sci. 1981 Jun;60(6):1132–1139. doi: 10.3382/ps.0601132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clurman B. E., Hayward W. S. Multiple proto-oncogene activations in avian leukosis virus-induced lymphomas: evidence for stage-specific events. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2657–2664. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. M., Neiman P. E. Two distinct candidate transforming genes of lymphoid leukosis virus-induced neoplasms. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):857–858. doi: 10.1038/292857a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crittenden L. B., Witter R. L., Okazaki W., Neiman P. E. Lymphoid neoplasms in chicken flocks free of infection with exogenous avian tumor viruses. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1979 Jul;63(1):191–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Lomedico P. T., Ju G. Transcriptional interference in avian retroviruses--implications for the promoter insertion model of leukaemogenesis. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):241–245. doi: 10.1038/307241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H. Cancer genes: rare recombinants instead of activated oncogenes (a review). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2117–2124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H. Retroviruses as carcinogens and pathogens: expectations and reality. Cancer Res. 1987 Mar 1;47(5):1199–1220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Zhou R. P., Goodrich D. Cancer genes by illegitimate recombination. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;567:259–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb16477.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. K., Fadly A. M., Crittenden L. B., Kung H. J. On the mechanism of retrovirus-induced avian lymphoid leukosis: deletion and integration of the proviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3418–3422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. K., Lewis W. G., Crittenden L. B., Kung H. J. Activation of the cellular oncogene c-erbB by LTR insertion: molecular basis for induction of erythroblastosis by avian leukosis virus. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):357–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90417-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C. The first human retrovirus. Sci Am. 1986 Dec;255(6):88–98. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican1286-88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenow M. M., Hayward W. S. 5' long terminal repeats of myc-associated proviruses appear structurally intact but are functionally impaired in tumors induced by avian leukosis viruses. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2489–2498. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2489-2498.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanter M. R., Smith R. E., Hayward W. S. Rapid induction of B-cell lymphomas: insertional activation of c-myb by avian leukosis virus. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1423–1432. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1423-1432.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M., Groudine M. Transcription of three c-myc exons is enhanced in chicken bursal lymphoma cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):53–57. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. A., Bryan T., Rasheed S., Khan A. S. Identification and cloning of endogenous retroviral sequences present in human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4892–4896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel B. G., Gasic G. P., Rogler C. E., Skalka A. M., Ju G., Hishinuma F., Papas T., Astrin S. M., Hayward W. S. Molecular analysis of the c-myc locus in normal tissue and in avian leukosis virus-induced lymphomas. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):158–166. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.158-166.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel B. G., Hayward W. S., Robinson H. L., Fang J., Astrin S. M. Avian leukosis virus-induced tumors have common proviral integration sites and synthesize discrete new RNAs: oncogenesis by promoter insertion. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne G. S., Courtneidge S. A., Crittenden L. B., Fadly A. M., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Analysis of avian leukosis virus DNA and RNA in bursal tumours: viral gene expression is not required for maintenance of the tumor state. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):311–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90127-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucho M., Hanahan D., Wigler M. Genetic and physical linkage of exogenous sequences in transformed cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):309–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90178-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaff S. L., Duesberg P. H. Two autonomous myc oncogenes in avian carcinoma virus OK10. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3703–3709. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3703-3709.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBIN H. Conditions for establishing immuno logical tolerance to a tumor virus. Nature. 1962 Jul 28;195:342–345. doi: 10.1038/195342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBIN H., FANSHIER L., CORNELIUS A., HUGHES W. F. Tolerance and immunity in chickens after congenital and contact infection with an avian leukosis virus. Virology. 1962 May;17:143–156. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90091-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines M. A., Lewis W. G., Crittenden L. B., Kung H. J. c-erbB activation in avian leukosis virus-induced erythroblastosis: clustered integration sites and the arrangement of provirus in the c-erbB alleles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2287–2291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins D. M., Ripley S., Henderson A. S., Axel R. Transforming DNA integrates into the host chromosome. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):29–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins T., Bister K., Garon C., Papas T., Duesberg P. Structural relationship between a normal chicken DNA locus and the transforming gene of the avian acute leukemia virus MC29. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):635–642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.635-642.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. L., Gagnon G. C. Patterns of proviral insertion and deletion in avian leukosis virus-induced lymphomas. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):28–36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.28-36.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. E., Tizard R., Gilbert W. Nucleotide sequence of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):853–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C. K., Linial M., Goodenow M. M., Hayward W. S. Nucleotide sequence 5' of the chicken c-myc coding region: localization of a noncoding exon that is absent from myc transcripts in most avian leukosis virus-induced lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4697–4701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift R. A., Boerkoel C., Ridgway A., Fujita D. J., Dodgson J. B., Kung H. J. B-lymphoma induction by reticuloendotheliosis virus: characterization of a mutated chicken syncytial virus provirus involved in c-myc activation. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2084–2090. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2084-2090.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., Reddy E. P., Duesberg P. H., Papas T. S. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the chicken c-myc gene reveals homologous and unique coding regions by comparison with the transforming gene of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29, delta gag-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2146–2150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway D., Payne G., Varmus H. E. Proviral deletions and oncogene base-substitutions in insertionally mutagenized c-myc alleles may contribute to the progression of avian bursal tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):843–847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkerson V. W., Bryant D. L., Parsons J. T. Rous sarcoma virus variants that encode src proteins with an altered carboxy terminus are defective for cellular transformation. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):314–321. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.314-321.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
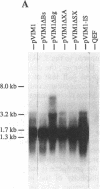
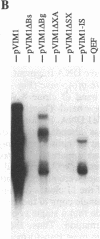
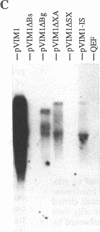
- Zhou R. P., Duesberg P. H. myc protooncogene linked to retroviral promoter, but not to enhancer, transforms embryo cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2924–2928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]