Fig. 5.
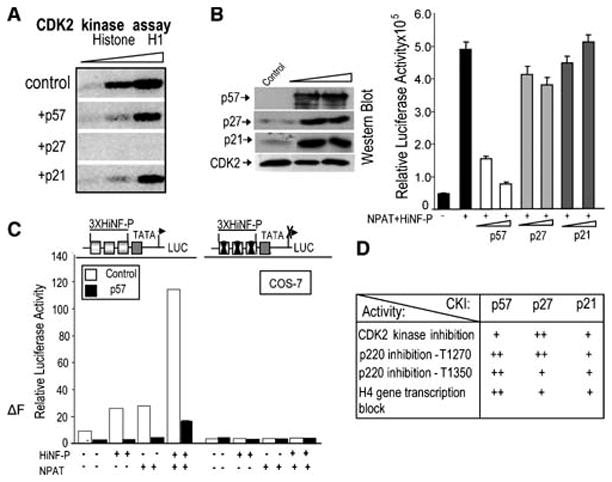
Inhibition of CDK2 kinase activity and H4 gene transcription by p57KIP2. (A) In Cos7 lysates, p27KIP1 is more potent than p57KIP2 or p21WAF1/CIP1 in blocking CDK2 activity. CDK2 kinase activity was measured using γ-32P-ATP and histone H1 as a substrate in CDK2 immunoprecipitates (respectively, 2, 5 and 10 μl of beads) obtained with lysates of mock-transfected cells or cells expressing p57KIP2, p27KIP1 or p21WAF1/CIP1. (B) Selective inhibition of HiNF-P/p220NPAT signaling at the H4 promoter by p57KIP2. Co-transfection experiments with a wild type H4 promoter-luciferase reporter gene in the absence (first bar) or presence of vectors for HiNF-P (200 ng/well) or p220NPAT (150 ng/well) (remaining bars) in cells expressing exogenous CKIs (25 or 50 ng vector) as indicated. H4 promoter-luciferase activities were measured within 24 h after transfection and plotted as a function of p57KIP2 vector concentration (right panel). Western blot analysis (left panel) was used to examine CKI expression in whole cell lysates (20 μg protein). Note that Cos7 cells do not express endogenous p57KIP2. (C) The HiNF-P binding site is sufficient for p57KIP2 dependent inhibition of the H4 gene promoter. Cos7 cells were co-transfected with Luciferase reporters controlled by wild type or mutant HiNF-P elements fused to a minimal TATA box promoter. Relative promoter activity was assessed in the presence (+) or absence (−) of vectors expressing HiNF-P, p220NPAT or p57KIP2 (25 ng/ml) as above. (D) Summary of data presented in Figs. 1 to 3 with + signs indicating the relative effectiveness of CKIs to affect the activities in the left column.
