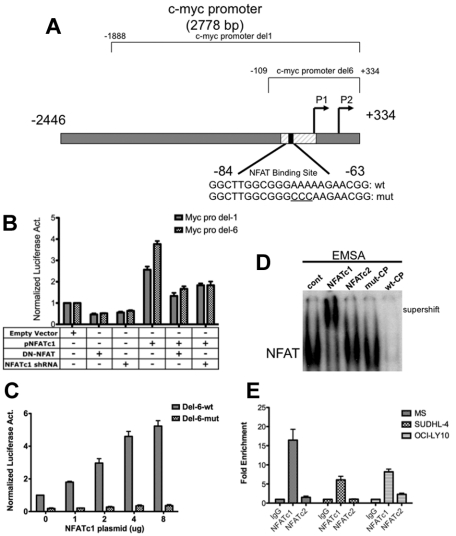
Figure 3.
NFATc1 binds to and regulates c-myc promoter in DLBCL. (A) Schematic diagram of the c-myc promoter. c-myc Del-1 and Del-6 are luciferase reporter constructs obtained from Addgene. (B) DLBCL MS cells were cotransfected with a c-myc Del-1 or Del-6 construct (2 μg) and an empty vector (5 μg) or a plasmid containing NFATc1 (5 μg, alone or combined with dominant-negative NFAT or NFATc1 shRNA). The NFATc1 shRNA is retained in the NFATc1 expression construct. Luciferase activities were analyzed 24 hours after transfection. Data indicate fold-induction compared with empty vector alone. Luciferase activities were normalized with β-gal activity. Data represent 3 independent experiments. (C) DLBCL MS cells were cotransfected with c-myc promoter Del-6 (2 μg) or c-myc promoter Del-6 with a mutated NFAT binding site (Del-6 mut; 2 μg) with increasing NFATc1 plasmid, as indicated. Luciferase activities were measured 24 hours after transfection. Luciferase activities were normalized with β-gal activity. Data represent 3 independent experiments. (D) DLBCL MS nuclear extracts were subjected to gel-shift assays using the 32P-labeled NFAT-binding site within the proximal end of the c-myc promoter. NFATc1 and NFATc2 antibodies were used for supershift. wt-CP, wild-type cold probe; mut-CP, mutant cold probe. (E) ChIP analysis in MS, SUDHL-4, and OCI-LY10 cells using antibodies to NFATc1, NFATc2, and IgG (negative control), followed by Q-PCR of the c-myc promoter (NFAT binding site). Input (10% of total DNA). Values indicate fold-enrichment over IgG control from 2 independent experiments with triplicate samples.