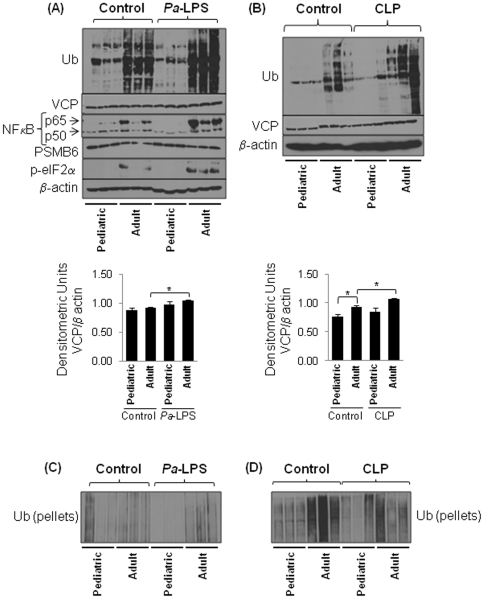
Figure 2. Early-age-related changes in proteostasis induce inflammation.
The total protein lung- (A) and liver- (B) lysates from control, CLP or i.t. (1 µg/gm bw) Pa-LPS induced murine model (n = 3) were immunoblotted for Ub (ubiquitin), PSMB6 (proteasome-subunit), VCP (UPR), NFκB (Inflammation), p-eIF2α (protective stress response) and β-actin. (A) The adult mice lungs show constitutive increase in NFκB and p-eIF2α levels and accumulation of ubiquitinated-proteins while levels of proteasomal subunit, PSMB6 decrease. The Pa-LPS further induces the levels of these proteins and VCP in adult mice while PSMB6 is lower indicating that proteostasis-imbalance in adult subjects is a critical early-age-related change that may induce immunopathogenesis of chronic- of fatal- injury in older subjects. (B) The liver shows a constitutive increase in VCP expression in the adult mice which correlates with higher accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins. The bottom panel (A & B) shows the densitometric analysis of VCP expression in both lung and liver normalized to β-actin (Mean ± SEM, n = 3, *p<0.05). (C & D) Of note here, both lung (C) and liver (D) also show accumulation of ubiquitinated-proteins in the insoluble protein fraction of adult mice as compared to the pediatric (n = 3) but lungs have relatively less accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins in insoluble fraction as compared to the liver. The early-age-related proteostasis-imbalance induces NFκB mediated inflammatory response.