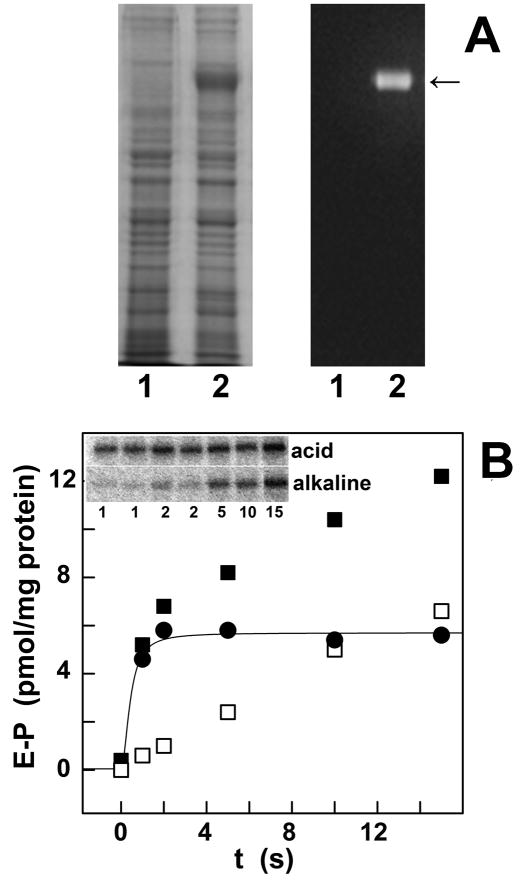
Fig 3.
Heterologous expression of ATP7B (A), and phosphorylation by ATP (B). (A): Electrophoretic analysis of the microsomal fraction of sham COS1 cells (left in each panel) and COS1 cells sustaining heterologous expression of ATP7B (right in each panel), followed by general staining of proteins with Coomassie Blue (left panel), and specific immunostaining of the expressed ATP7B protein using a monoclonal antibody for a c-myc tag (right panel). (B): Phosphorylation of ATP7B was obtained by addition of (γ-32P)ATP, followed by acid quenching at times specified in the figure (inset). The quenched protein was then dissolved in detergent, and subjected to electrophoretic analysis in acid or in alkaline media to detect total phosphoprotein (■), and distinguish alkaline labile (●, aspartyl phosphate) and alkaline stable (□, phosphorylated serines) fractions.