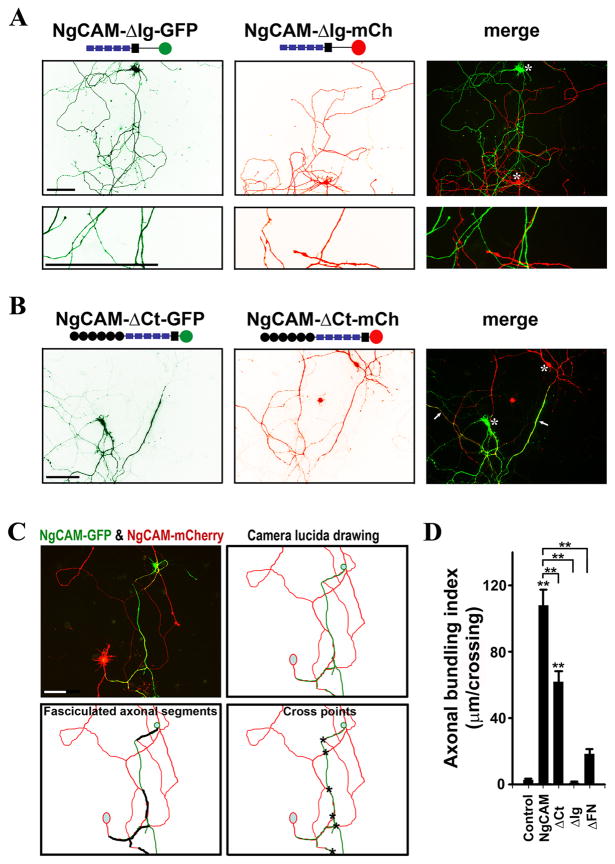
Fig. 2. Distinct roles of Ig and C-terminal domains of NgCAM in axonal bundling.
(A) Deleting the Ig domains eliminated NgCAM-induced axonal bundling. Almost no axonal bundling was observed between NgCAM-ΔIg-GFP- and NgCAM-ΔIg-mCh-expressing neurons. NgCAM-ΔIg-GFP (green) and NgCAM-ΔIg-mCh (red) were transfected into different neurons at 5DIV and fixed three days later. (B) Deleting the intracellular C-terminal domain of NgCAM (NgCAM-ΔCt) moderately reduced axonal bundling. Axonal bundles were still abundantly present in culture. (C) Diagram for calculating the axonal bundling index (ABI). A pair of neurons expressing NgCAM-GFP (green) and NgCAM-mCherry (red) had bundled axonal segments. The camera lucida drawing is at the upper-right panel. Segments of axonal bundles are shown with thick black lines (lower left) and the crossings between green and red axons are indicated with asterisks (lower right). The ABI (104μm/crossing) of this pair of neurons equals to the total length of axonal bundles (624 μm) divided by the total number of crossings (6). (D) Summary of ABIs of NgCAM truncations. Control, between axons of GFP- and mCherry-expressing neurons; NgCAM, between axons of NgCAM-GFP- and NgCAM-mCherry-expressing neurons;ΔCt, between axons of NgCAM-ΔCt-GFP- and NgCAM-ΔCt-mCh-expressing neurons; ΔIg, between axons of NgCAM-ΔIg-GFP- and NgCAM-ΔIg-mCh-expressing neurons; ΔFN, between axons of NgCAM-ΔFN-GFP and NgCAM-ΔFN-mCh-expressing neurons. Asterisks, soma of transfected neurons. Scale bars, 100 μm. One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test was used for the comparison to the control group; ** P < 0.01. Additional One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test was performed for comparing the truncations to the wild type NgCAM shown on the top; ** P < 0.01.