Fig 1.
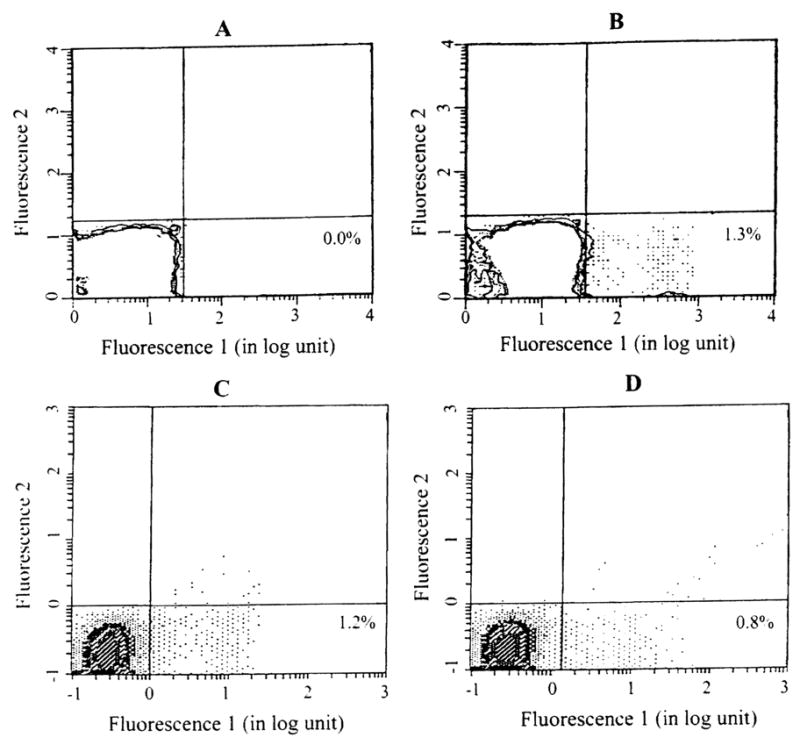
Donor chimerism in the peripheral blood leukocytes of a lung recipients who received bone marrow infusion. Recipient cells were stained with a primary mouse antibody against human MHC class I, then counterstained with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) conjugated goat anti-mouse secondary antibody, and analyzed using an EPICS Elite Flow Cytometer (Coulter Corp, Hialeah, FL). (A) Before transplantation; (B) 1 month, (C) 6 months, and (D) and 9 months after transplantation. The number in the right lower quadrant indicates the percentage of donor cells. The level of chimerism was higher after transplantation, but dwindled with time.
