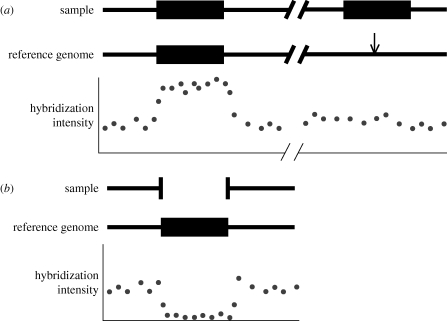
Figure 1.
Detecting duplications and deletions relative to a reference genome using hybridization intensities. (a) When a region of the genome has one copy in the reference genome but two copies in the sample (black rectangles), DNA from both paralogues in the sample hybridize to probes corresponding to the only copy in the reference, resulting in a spike in hybridization intensity at these probes (illustrated by the elevated intensities directly below the copy in the reference). The location of the additional copy present in the sample genome is denoted with an arrow in the reference genome. (b) When a region of the genome has one copy in the reference genome (black rectangle) but no copies in the sample, hybridization intensity is significantly diminished at probes corresponding to the sequence missing from the sample.