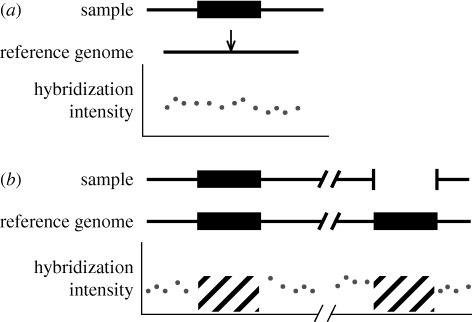
Figure 4.
Hybridization-based methods will not detect either deletions in the reference or highly similar duplications in the reference. As in figure 1, sample hybridization intensities are shown under the corresponding regions of the reference genome. (a) If a deletion allele is present in the reference genome (the location is shown by the arrow), then an array designed from the reference will not be able to probe this sequence in sample individuals. (b) If a duplication allele is present in the reference genome, arrays designed from the reference will probably not probe these repetitive regions (shown as diagonal black lines). Because of ambiguous sequence mapping, next-generation sequencing methods will also have difficulty detecting variants in these regions.