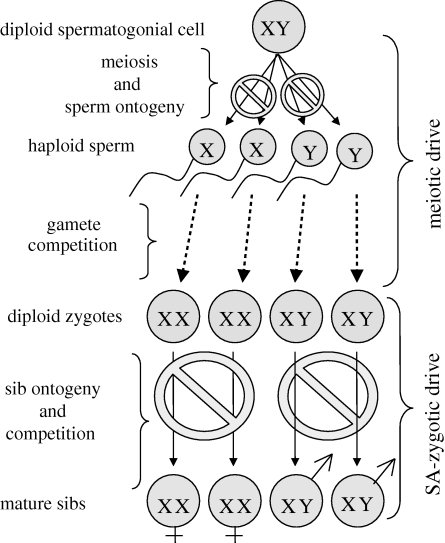
Figure 1.
Meiotic versus SA-zygotic drive. Sperm competition provides the selective environment for the evolution of meiotic drive of the sex chromosomes. In this context, each sex chromosome is selected to disrupt (circular stop symbols) the post-meiotic ontogeny of the type of gamete (X- or Y-bearing) that does not carry it. Sib competition provides the selective environment for the evolution of SA-zygotic drive. In this context, each sex chromosome is selected to disrupt (circular stop symbols) the post-zygotic ontogeny of the type of offspring (male or female) that does not carry it. This disruption can be mediated by sex-specific (i) epigenetic paternal effects, (ii) sib–sib interactions, (iii) paternal investment, and as shown here, (iv) grandparental investment. The strong functional similarity with meiotic drive, but operating during diploid rather than haploid ontogeny, motivates the term ‘SA-zygotic drive’.