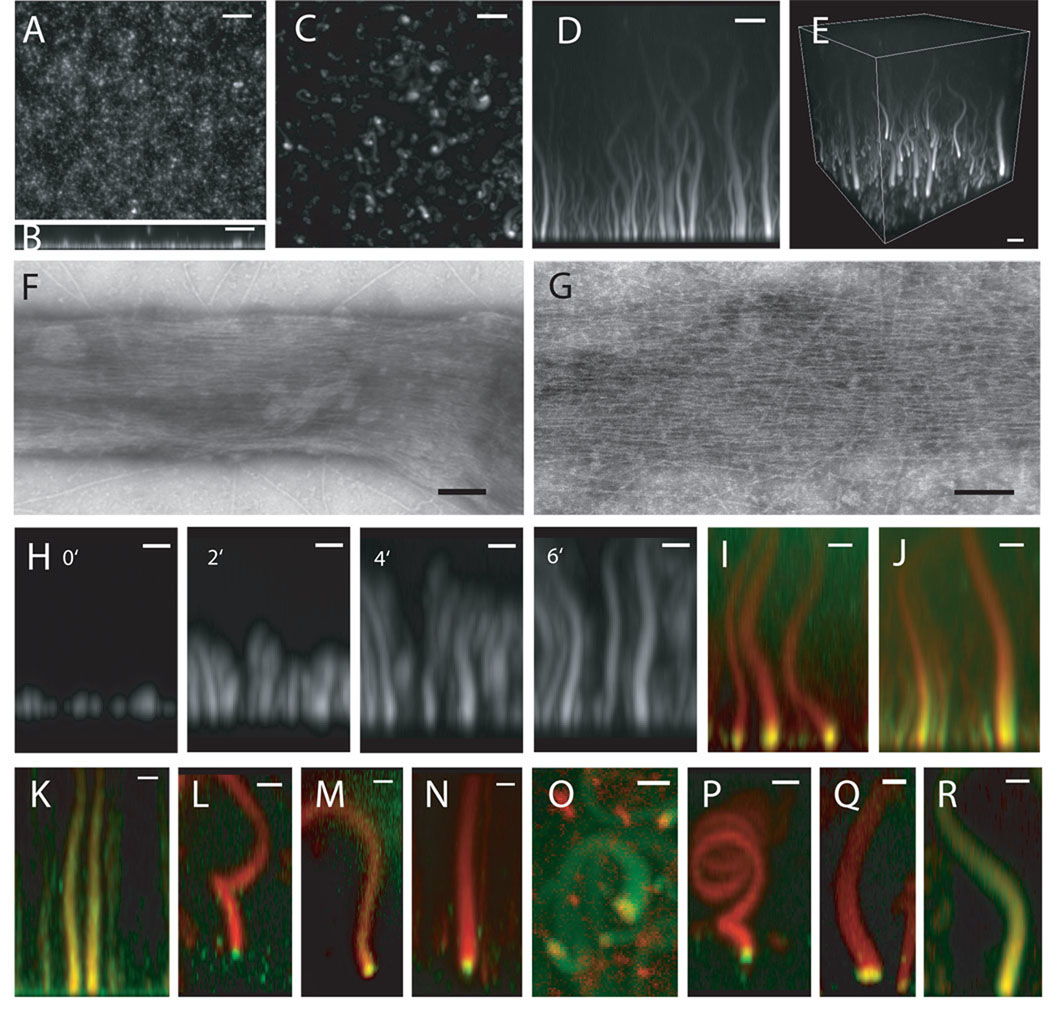
Figure 1. Reconstitution of filopodia-like structures on supported lipid bilayers containing 45% PC (Phosphatidylcholine), 45% PI (Phosphatidylinositol), 10% PI(4,5)P2.
(A) Confocal microscopy of supported bilayers with Cdc42, N-WASP-WIP, toca-1, Arp2/3 complex, and actin generates uniform, short polymerized actin. (B) Z-stack reconstruction of (A) showing growth of actin in the z-axis. (C) Confocal microscopy of supported lipid bilayers with Xenopus egg extracts and Alexa647-actin (seen in x–y) shows growth of focal actin structures from the bilayer in the z-axis. (D) Z-stack reconstruction of x–z shows the height of the actin structures. (E) 3D reconstruction. Bars: 5 µm. (F–G) Negative-stain electron microscopy of the phalloidin-stabilized actin structures shows that these are made of bundled, unbranched actin filaments Bars: 100 nm (H) Time-lapse sequence of FLS formation seen. Bars: 2 µm. (I and J) Pulse-chase experiments show that actin polymerization occurs at membrane. The reaction is started with Alexa 647-actin (red) and chased by Alexa 488-actin (green). Bars: 2 µm. (I) 1 min timepoint. (J) 2 min 40 sec timepoint. (K) Immunostained FLSs from the side, green: fascin immunostain, red: Alexa568-phalloidin (L) 60 degree tilt from x–y, green: Drf1 immunostain, red: Alexa568-phalloidin (M) 60 degree tilt from x–y, green: GFP-VASP, red: Alexa 647-actin (N) 60 degree tilt from x–y, green: profilin immunostain, red: Alexa568-phalloidin (O) top view, red: mCherry-Cdc42, green: Alexa 488-actin (P) 60 degree tilt from x–y, green: N-WASP immunostain, red: Alexa568-phalloidin (Q) tilted view, green: GFP-toca-1, red: Alexa 647-actin (R) side view, red: Alexa 568-Arp2/3 complex, green: Alexa 647-actin. Bars: 2 µm.